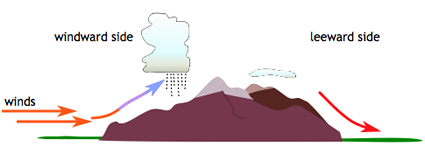
When wind blows across a mountain range, air rises and cools and clouds can form.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of CMMAP
Cloud Formation Due to Mountains
Some clouds form when air encounters a mountain range or other types of terrain. When this happens, the air will rise and cool. The cooler air is no longer able to hold all of the water vapor it was able to hold when it was warm. This extra water vapor begins to condense out of the air parcel in the form of liquid water droplets and a cloud is formed.
The types of clouds that form from encounters with mountains are stratus clouds and lenticular clouds.
The image on this page shows how winds can blow into a mountain range and then rise higher in the atmosphere. The side of the mountains where the wind starts is called the windward side. The side of the mountains where the wind leaves the area is called the leeward side.
Another way that mountains cause cloud formation is when air rises because the mountain is warmer than the surrounding air and causes the air to rise. Once the air rises, it follows the same process to form clouds as described above. The types of clouds that form in this case are cumulonimbus (and associated mammatus clouds), and cumulus.
You might also be interested in:

Condensation is the process by which water changes its state from a vapor or gas to a liquid. Condensation is responsible for the formation of clouds. Common examples of condensation are: dew forming on
...more
Stratus (weather symbol - St) clouds consist of water droplets and belong to the Low Cloud (surface-2000m up) group. They are uniform gray in color and can cover most or all of the sky. Stratus clouds
...more
Lenticular clouds form on the downwind side of air flowing over a large mountain or mountain range. Unlike most clouds that move across the sky, lenticular clouds stay in one place as air appears to blow
...more
Wind is moving air. Warm air rises, and cool air comes in to take its place. This movement creates different pressures in the atmosphere which creates the winds around the globe. Since the Earth spins,
...more
Cumulonimbus (weather symbol - Cb) clouds belong to the Clouds with Vertical Growth group. They are generally known as thunderstorm clouds. A cumulonimbus cloud can grow to such heights that it actually
...more
Mammatus clouds are pouches of clouds that hang underneath the base of a cloud. They are most often associated with cumulonimbus clouds, and they indicate that a storm is particularly strong. These clouds
...more
Cumulus (weather symbol - Cu) clouds belong to the Clouds with Vertical Growth group. They are puffy white or light gray clouds that look like floating cotton balls. Cumulus clouds have sharp outlines
...more