Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of K. Trenberth, J. Fasullo, and J. Kiehl.
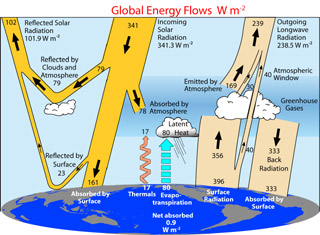
Earth's Radiation Budget
Sunlight streams into Earth's atmosphere from space. Some is reflected away by clouds and snow-covered landscapes. Light that makes it to the ground is absorbed and heats Earth's surface and oceans. The warm ground and water emits infrared (IR) radiation. Most of that IR "light" is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, warming the air. Some of it eventually escapes back into space. Scientists call this balancing act between incoming solar energy and outgoing heat "Earth's radiation budget".
The diagram on this page provides more details about our planet's radiation budget. Radiation, in this sense, isn't the stuff of atom bombs and nuclear power plants. Instead, it is electromagnetic radiation; mostly in the form of visible light and infrared radiation. Scientists measure it in units of watts per square meter (W/m2 or W·m-2). Imagine laying out a square on the ground that is one meter on a side and then tracking how much solar energy falls on that square each second - you get the picture! On average, over the entire surface of Earth during a whole day, about 341.3 W/m2 of sunlight energy reaches the top of the atmosphere from the Sun.
Much of that incoming sunlight is reflected away by clouds or absorbed by the atmosphere. Some of the light that reaches the surface is also reflected away, especially by light-colored terrain covered by snow or ice. Slightly less than half (about 161 W/m2) is absorbed by the planet's surface, including the oceans. Warm objects emit IR radiation, as shown on the right in the diagram. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are nearly transparent to visible light, but are almost opaque at IR wavelengths. Our atmosphere serves as a planetary blanket; Earth's average temperature would be about 30° C (54° F) colder if there was no greenhouse effect! Eventually the outgoing IR energy leaks into space.
For the most part, the energy coming into the Earth system equals the energy flowing back out. If that wasn't the case, Earth would gradually grow warmer or cooler. At times in our planet's history this balance was slightly off, causing the global climate to change. Lately, as the greenhouse gases in our atmosphere have increased, the balance has been thrown slightly off. Earth's climate is gradually warming. Scientists keep a close watch on the overall radiation budget to help them better understand and predict global warming.