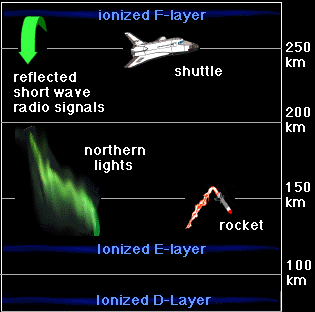
This image shows how the ionosphere is divided even further into layers: D, E, and F layers.
Click on image for full size
Windows to the Universe original image
Regions of the Ionosphere
The ionosphere can be further broken down into the D, E and F regions. The breakdown is based on what
wavelength of solar radiation is absorbed in that region most frequently or on what level of radiation is needed to photodissociate the molecules found in these individual regions.
The D region is the lowest in altitude, though it absorbs the most energetic radiation, hard x-rays. The D region doesn't have a definite starting and stopping point, but includes the ionization that occurs below about 90km (or ionization that occurs below the E region).
The E region peaks at about 105km. It absorbs soft x-rays.
The F region starts around 105km and has a maximum around 600km. It is the highest of all of the regions. Extreme ultra-violet radiation (EUV) is absorbed there.
On a more practical note, the D and E regions (the lower parts of the ionosphere), reflect standard AM radio waves back to Earth. Radio waves with shorter lengths are reflected by the higher F region. Visible light, radar, television and FM wavelengths are all too short to be reflected by the ionosphere. So these types of global communication are made possible by satellite transmissions.
You might also be interested in:

Imagine you found a pair of special glasses that not only gave you telescopic vision but gave you the ability to see all forms of radiant energy. The universe in visible light contains all the familiar
...more
The thermosphere is a layer of Earth's atmosphere. The thermosphere is directly above the mesosphere and below the exosphere. It extends from about 90 km (56 miles) to between 500 and 1,000 km (311 to
...more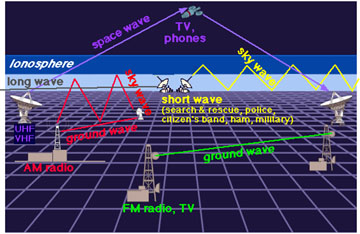
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. A radio wave has a much longer wavelength than does visible light. We use radio waves extensively for communications. Radio waves have wavelengths as
...more
Rainbows appear in the sky when there is bright sunlight and rain. Sunlight is known as visible or white light and is actually a mixture of colors. Rainbows result from the refraction and reflection of
...more
The Earth travels around the sun one full time per year. During this year, the seasons change depending on the amount of sunlight reaching the surface and the Earth's tilt as it revolves around the sun.
...more
Scientists sometimes travel in specially outfitted airplanes in order to gather data about atmospheric conditions. These research aircraft have special inlet ports that bring air from the outside into
...more
An anemometer is a weather instrument used to measure the wind (it can also be called a wind gauge). Anemometers can measure wind speed, wind direction, and other information like the largest gust of wind
...more