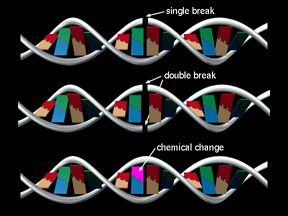
Radiation can damage DNA molecules in three ways: by causing a single strand break, a break in both strands, or a chemical change or mutation. A single strand break can often be repaired by the cell. The other two types of damage usually cannot be repaired.
Click on image for full size
Source unknown.
Can living cells repair damage from radiation?
Whether or not a cell can repair itself after being damaged by radiation depends on the type of damage to the cell's DNA.
| Type of Damage |
Prospects for DNA Repair |
| Single strand break in the DNA |
Can usually be repaired and normal cell function restored. |
| Breaks in both DNA strands |
Usually damage is too severe for repair. The cell dies. |
| Chemical change or mutation |
Cannot be repaired. Cancer may result or a mutated offspring if this occurs in a sperm or egg cell. |
Cells (such as those contained in the skin, eyes and blood-forming organs [BFO]) that reproduce rapidly are the most susceptible to damage because they cannot repair themselves easily while replicating. Acceptable radiation doses are usually given separately for these organs.
You might also be interested in:
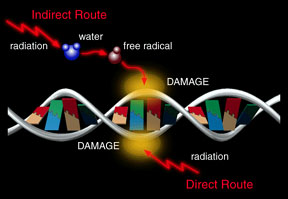
High frequency radiation or fast moving particles plow into a living cell with enough energy to knock electrons free from molecules that make up the cell. These molecules with missing electrons are called
...more
The text for this level hasn't been written yet. Please check the "Intermediate" or "Advanced" level of this page (click on the bar near the top of this page).
...more
Jupiter's atmospheric environment is one of powerful winds, going 250 miles per hour, and temperatures from -270 degrees to +32 degrees (freezing temperature). These winds make it hard for life forms to
...more
In July, 1996 a team of scientists said that they had discovered possible fossils of bacteria in a meteorite named ALH84001 that came from Mars. It was found in Antarctica in 1984 after having landed there
...more
Saturn's atmospheric environment is one of powerful winds, going 250 miles per hour, and temperatures from -270 degrees to +80 degrees. With winds like these, it is hard to have peace and quiet. The region
...more
The air of Titan is a lot like the Earth's, except that it is very cold, from -330 degrees to -290 degrees! Like the Earth, there is a lot of Nitrogen and other complex molecules. There also may be an
...more
Organisms that are able to "make their own food" are called autotrophs, meaning "self-feeders". Some examples of autotrophs are plants and algae (shown in the picture). Both plants and algae use photosynthesis
...more