An electron micrograph of Bacteria
Image courtesy of JPL/NASA
The First Living Cells
The first beings were probably much like
coacervates.
As
a group, these bacteria are called
heterotrophic anaerobes.
Because there was virtually no oxygen in the atmosphere at
this time, these bacteria were necessarily
anaerobic,
meaning they did not breathe oxygen.
Heterotrophs, meaning "other feeders", are simply organisms that
cannot make their own food. The
fossils of some these oldest known forms of life
have been found in Australian rocks dating back 3.5 billion years.
To create energy, these early bacteria probably used a chemical process called enzymatic catalysis to consume naturally occurring amino
acids, sugars, and other organic compounds that had
formed spontaneously in the atmosphere then dissolved in liquid water. Because of this chemical process, scientists sometimes call these beings chemo-heterotrophic anaerobes. Upon digestion of these molecules, early bacteria produced methane and carbon dioxide as waste products. Fermenting bacteria would be today's analog of these early creatures. To make beer, barley or wheat is combined with water to make a carbohydrate mash. Bacteria eat the sugars and produce alcohol and CO2 as waste products. In the early Earth, the alcohol and carbon dioxide became part of the natural environment.
Over time, new life forms evolved which were
able to get their energy from a different source -- the Sun!
You might also be interested in:
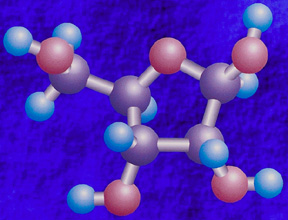
In the warm primordial ocean, aggregates of amino acids, proteins, and other hydrocarbons coalesced into a form called *coacervates*. Organic polymers such as amino acids will spontaneously form coacervates
...more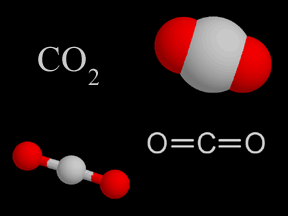
Carbon dioxide is a colorless and non-flammable gas at normal temperature and pressure. Although much less abundant than nitrogen and oxygen in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide is an important constituent
...more
Organisms that are able to make their own food (in the form of sugars) by using the energy of the Sun are called autotrophs, meaning "self-feeders". Photosynthesis is the name of the process through which
...more
Eventually, as with the development of photosynthesis along sulfur and methane pathways, where sulfur and methane products are produced, photosynthesis along the oxygen pathway, where oxygen is produced,
...more
In August 2009, scientists reported finding a type of amino acid in a sample returned from a comet. Amino acids are the building-blocks of proteins, one of the key molecules in living creatures. The comet
...more
Jupiter's atmospheric environment is one of strong gravity, high pressure, strong winds, from 225 miles per hour to 1000 miles per hour, and cold temperatures of -270 degrees to +32 degrees (freezing temperature).
...more
In July, 1996, it was announced that Dr. David McKay, along with a team of scientists at Johnson Space Center (a division of NASA), had discovered possible fossils of bacteria in an ancient rock from Mars.
...more















