A polar bear is just one example of an organism that uses respiration to gain biochemical energy. Respiration occurs in all other animals too.
Click on image for full size
Corel Photography
Respiration
Respiration is the name of the general process by which living organisms
convert sugars and oxygen into biochemical energy. The process occurs
in
all organisms, including animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria (though
in some cases other electron acceptors, like nitrate, are substituted
for the oxygen). During respiration, carbohydrates are broken down, and
the energy stored in the carbohydrates' bonds is used to produce ATP and
other high-energy compounds that can be used throughout the cell to fuel
the different processes necessary to support life.
In addition to producing useful energy, respiration produces carbon
dioxide and water as waste products. The overall equation for the
process is given below:
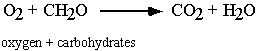
The reverse of this process, used by
autotrophs (self-feeders), is known
as photosynthesis. During
photosynthesis, energy from the Sun's rays is
used by cells to produce carbohydrates, with oxygen made as a byproduct.
You might also be interested in:

Autotrophs are organisms that produce organic compounds from an inorganic source of carbon (carbon dioxide) given a source of energy. If the source of energy is the reactions of inorganic chemical compounds,
...more
Photosynthesis is the name of the process by which autotrophs (self-feeders) convert water, carbon dioxide, and solar energy into sugars and oxygen. It is a complex chemical process by which plants and
...more
Eventually, as with the development of photosynthesis along sulfur and methane pathways, where sulfur and methane products are produced, photosynthesis along the oxygen pathway, where oxygen is produced,
...more
About 2.5 billion years ago (BYA), after the iron in the ocean was gone to form iron ore deposits, oxygen began accumulating in the atmosphere. Soon, enough oxygen accumulated in the early atmosphere for
...more
Nutrients from the Amazon River's outflow spread well beyond the continental shelf and drive carbon cycling in the tropical ocean, say scientists who conducted a multi-year study. They will publish their
...more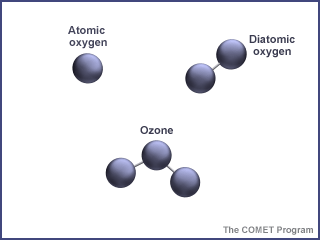
Ozone is a special kind of oxygen molecule. Normal oxygen molecules (O2), the kind we need to breathe, have two oxygen atoms. Ozone molecules (O3) have three oxygen atoms. Ozone forms when a photon of
...more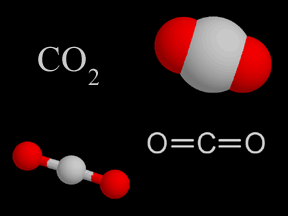
Carbon dioxide is a colorless and non-flammable gas at normal temperature and pressure. Although much less abundant than nitrogen and oxygen in Earth's atmosphere, carbon dioxide is an important constituent
...more
















