Click on image for full size
Image courtesy L. J. Lanzerotti, Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies, Inc.
Related links:
Explore Space Weather and the Sun-Earth System
Space Weather at Earth and in Near-Earth Space (Geospace)
Hands-on Activity: Build a Magnetometer
Movie: Supercomputer Models Help Scientists Understand Sunspots
When Nature Strikes: Space Weather
When Nature Strikes: You Be the Solar Scientist! Classroom Activity
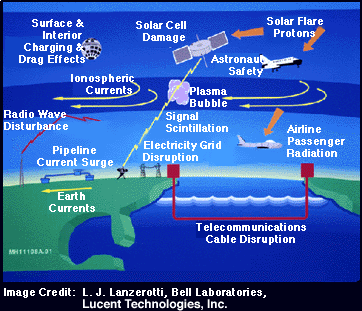
How Space Weather Affects Human Society
Space weather affects human society in many ways. Let's take a look at the ways in which radiation and magnetic disturbances in space can affect us here on Earth.
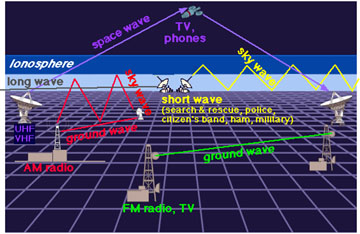
Space weather "storms" can disrupt radio communications on Earth. This includes all kinds of transmissions carried by radio waves, from television signals to airline communications to cell phone transmissions. GPS (Global Positioning Systems) also use radio signals from satellites; their accuracy can be diminished during space weather storms. The ionosphere, an electrically charged region in the atmosphere, has been used for decades to "bounce" radio signals to distant locations on Earth. Space weather alters the heights and densities of the layers of the ionosphere, changing their abilities to reflect radio waves.
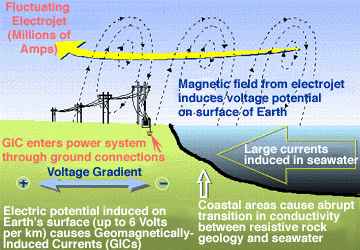
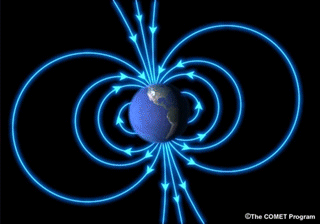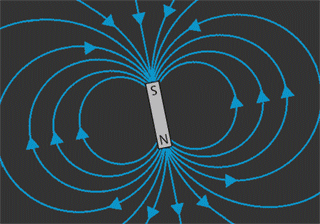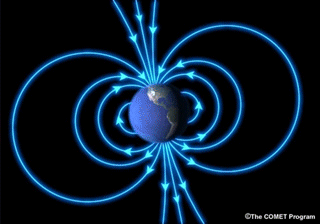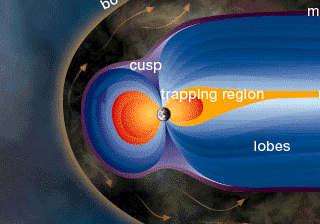
Space weather disturbances alter the magnetic field around Earth and can change the way electrical currents flow in Earth's atmosphere. These disruptions throw off compasses used in navigation. The disruptions can also generate problematic currents in wires used in our electrical grid, overloading transformers and causing blackouts. Space weather-induced electrical currents can also flow in metal pipes that carry oil and gas, causing increased corrosion which can lead to leaking and even ruptures. Magnetic disturbances also interfere with geologic prospecting, which often relies on sensitive instruments called "magnetometers" to detect the presence of ore deposits.
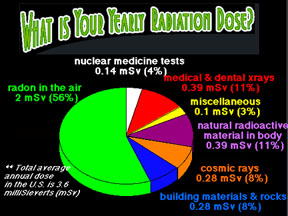
Various types of radiation are associated with space weather, and can produce health hazards to humans and other living creatures. As you might suppose, astronauts in space are at a much greater risk from radiation than are people on the ground. However, airline passengers and crews, especially on flights that take them near Earth's poles where radiation from space typically penetrates most deeply into the atmosphere, must also take precautions when space weather "storms" are especially active. Some animals, such as homing pigeons, are sensitive to magnetic fields and use that sensitivity to navigate on long journeys. The "natural compasses" of such creatures can be thrown out of whack when our planet's magnetic field is altered by space weather disturbances.
Satellites are vulnerable to major space weather disturbances. Radiation can damage electronics on satellites in several different ways, and can cause the premature "weathering" of the solar cells that power many spacecraft. Active space weather heats and "puffs up" Earth's upper atmosphere, generating drag on satellites that causes them to fall from orbit sooner than they otherwise would.
Not all space weather effects are bad, though. These "storms from space" can produce beautiful light shows called the aurora, or Northern and Southern Lights. The celestial light shows have fascinated people for ages, especially those (like the Inuit and Norse peoples) who dwell at high latitudes. The aurora have influenced myths, legends and art in Arctic cultures. For example, one Norse myth attributes the auroral lights to reflections from the shields of the warrior-maiden valkyries.