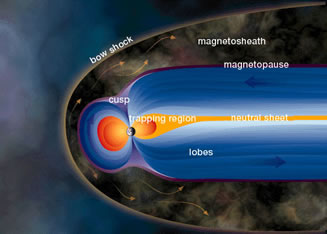
Charged Particle Motion in Earth's Magnetosphere
Charged Particle Motion in a Uniform Magnetic Field
A particle with charge ![]() moving
with velocity
moving
with velocity ![]() in
a uniform magnetic field
in
a uniform magnetic field ![]() experiences
a force:
experiences
a force:
![]()
The force on the particle is perpendicular to both the velocity and magnetic field and thus does no work on the particle.
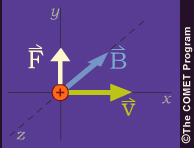
If the velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field, the particle
moves in a circle of radius ![]() with
centripetal acceleration
with
centripetal acceleration ![]() .
Equating the magnetic force to the particle mass
.
Equating the magnetic force to the particle mass ![]() times
the centripetal acceleration, we can show that the radius of gyration
(or gyroradius) of the particle is equal to
times
the centripetal acceleration, we can show that the radius of gyration
(or gyroradius) of the particle is equal to ![]() .
.
|
Click the question marks to see the formulation:
|
For a given gyroradius, the corresponding frequency of gyration (or
gyrofrequency), expressed in radians per second, is ![]() .
.
|
Click the question marks to see the expression:
|
If a component of the particle's velocity ( ![]() )
is parallel to the magnetic field, then
)
is parallel to the magnetic field, then ![]() is
replaced by
is
replaced by ![]() in
the preceding two equations, while the
in
the preceding two equations, while the ![]() component
carries the particle along the magnetic field, creating a helical trajectory.
component
carries the particle along the magnetic field, creating a helical trajectory.
|
|