Click on image for full size
Windows to the Universe
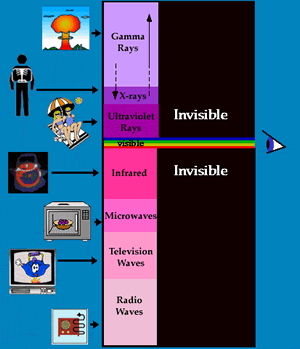
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: All Sorts of Light!
All types of radiation from the Sun are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Radiation travels in electromagnetic waves. The waves are called electromagnetic because the energy has both magnetic and electrical properties.
The spectrum usually is divided into seven types of radiation: radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, and gamma-ray radiation. Different types have different frequencies of waves. Whether the frequency is high or low, all electromagnetic waves travel at 300,000,000 meters per second. The characteristics of each type of radiation are described below.
Radio waves
These waves are used to bring you the tunes from your favorite radio station, but they are also a type of radiation from the Sun. Radio waves have the lowest frequency and longest wavelength of all waves in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Microwaves
Microwaves have a slightly smaller wavelength, thus higher energy than radio waves. Microwaves can be used to study the Universe, communicate with satellites in Earth orbit, and cook popcorn.
Infrared radiation
Infrared radiation has wavelengths longer than visible radiation and shorter than microwave radiation. Infrared radiation is commonly used by remote sensing instruments carried on satellites to detect vegetation cover, biological properties, geological formations, emissions from the Earth's atmosphere and water vapor in the atmosphere. Satellites can collect infrared radiation data at day or night because measurements are based on temperatures rather than visible radiation.
Visible radiation
That part of the electromagnetic spectrum which humans are able to see including the colors of the rainbow which, when combined, make white light. Within the spectrum of visible light, red light travels in broad, low frequency waves while violet light travels in smaller, high frequency waves.
Ultraviolet radiation
With slightly more energy than the violet end of the visible light spectrum, ultraviolet radiation makes up only about 5 percent of all energy from the Sun. Most ultraviolet radiation from the Sun is blocked by Earth's atmosphere, but some makes it through and aids in plant photosynthesis and helps produce vitamin D in humans. Too much ultraviolet radiation can burn the skin, cause skin cancer and cataracts, and damage vegetation.
X-ray radiation
X-rays are radiation with short wavelength and high-energy. They have shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet light but longer wavelengths than gamma rays. Because x-rays have more energy than visible light, they travel through materials like skin, tissue and organs bouncing off hard bone. That's how doctors use them to take photographs of bones.
Gamma-ray radiation
Gamma rays vibrate faster than any other type of radiation. That means that they are traveling with the shortest wavelengths.