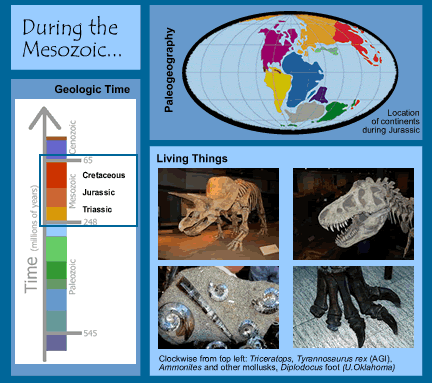
Characteristics of the Mesozoic
Click on image for full size
L.Gardiner/Windows to the Universe
Click on image for full size
L.Gardiner/Windows to the Universe
Happenings During the Mesozoic Era (248-65 Million Years Ago)
Time:248 to 65 million years ago
(See the geologic timescale!)
Paleogeography:
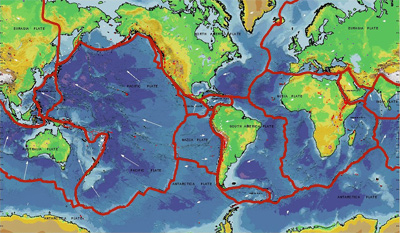
At the start of the Mesozoic, the continents were all joined together forming
one large continent called Pangaea. During Mesozoic time, they pulled apart
from one another. Continents move due to plate tectonics.
Climate:
- The climate most likely remained warm throughout the Mesozoic. No evidence of glaciations has been found in Mesozoic age rocks and abundant evidence of tropical species has been found in Mesozoic age fossils.
- During the last part of the Mesozoic (called the Cretaceous period) the climate warmed very much. Earth was several degrees warmer than it is today. There was much less variation in temperature between the equator and the poles at this time.
- There is strong evidence that global cooling occurred at the end of the
Mesozoic. The cooling may have been caused by either a huge asteroid impact
near the Yucatan Peninsula, a large amount of volcanic eruptions in the area
that is today India and Pakistan, or by a combination of both the asteroid
and volcanoes. The Sun would have been blocked for some time by the debris
spewed into the atmosphere.
Evolutionary Events:
- Dinosaurs evolved and became abundant! Some were herbivores (eating plants) while others were carnivores (eating meat). Dinosaurs were reptiles, however there is some evidence that they may have been warm-blooded.
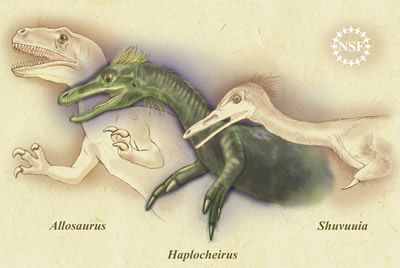
- Birds: During the late Mesozoic, birds evolved from a group of small carnivorous dinosaurs.
- Plants: Conifer trees evolved at the beginning of the Mesozoic. The first flowering plants evolved towards the end of the Mesozoic.
- Mammals evolved during the Mesozoic but there were relatively few species and they were small in size. During the Mesozoic, mammals were eaten by carnivorous dinosaurs.
- At the end of the Mesozoic, the Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction occurred.
This was the extinction event that killed the dinosaurs (among others). Many
of the animals and plants that survived the extinction event (such as mammals
and birds) went on to become very abundant afterward. Likely causes of the
extinction event include a large asteroid impact, erupting volcanoes, and
climate change. There is evidence that all three of these happened.
Last modified August 23, 2009 by Jennifer Bergman.