Blocks of frozen ground, known as permafrost, break off into the ocean as the ground thaws along coast of Canada
Natural Resources Canada, Earth Sciences Sector
The Warming Arctic
In the north polar region, the climate has warmed rapidly during the past few decades. Average temperatures in the Arctic are rising twice as fast as they are elsewhere in the world. In Alaska (USA) temperatures have increased on average 3.0°C (5.4°F) between 1970 and 2000.
The Arctic is showing some of the most dramatic effects of global warming. Glaciers, including parts of Greenland’s massive ice sheet, are melting rapidly. Sea ice covers less of the Arctic Ocean each summer. Snow blankets some areas for less of the year. Thawing of frozen ground, called permafrost, is releasing methane, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere and is causing damage to buildings and roads. Along the coast, thawing permafrost is causing shoreline sediments to slump into the seawater, like in the picture at the left.
There have been noticeable changes in plant and animals populations in the Arctic too. Some species are moving further north to be where it is cooler. For example, there are more shrubs growing in the tundra of Alaska and trees are able to grow further north. Other species have experienced population booms or declines. Peary caribou in northern Canada have declined from 24000 in 1961 to perhaps as few as 1100 in 1997 because there have been years where food was limited. Polar bear populations may be declining because melting sea ice limits their hunting opportunities. Meanwhile, in Alaska, spruce bark beetles are breeding faster than ever in the warmer climate. From 1993 to 2003 the oversized beetle population chewed up 3.4 million acres of forest trees.
Last modified March 4, 2008 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

North of the Arctic Circle (at 66.5°N latitude) you will find the Arctic Ocean surrounded by the northernmost parts of the continents of Europe, Asia, and North America. You will find the geographic North
...more
Sea ice is frozen seawater. It can be several meters thick and it moves over time. Although the salts in the seawater do not freeze, pockets of concentrated salty water become trapped in the sea ice when
...more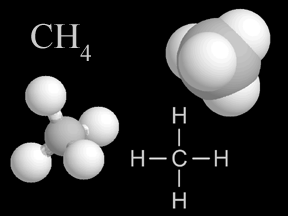
Methane is gas that is found in small quantities in Earth's atmosphere. Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas.
...more
Less than 1% of the gases in Earth's atmosphere are called greenhouse gases. Even though they are not very abundant, these greenhouse gases have a major effect. Carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O),
...more
The Arctic tundra, vast plains filled with grasses, flowers, mosses and lichen, is located north of the taiga forests in Earth’s north polar region. Like all types of tundra, this is a very cold and windy
...more
“Polar bears are one of nature’s ultimate survivors, able to live and thrive in one of the world’s harshest environments, but we are concerned the polar bears’ habitat may literally be melting” said US
...more
The world has several oceans, the Pacific, the Atlantic, the Indian, the Arctic, and the Southern Ocean. While we have different names for them, they are not really separate. There are not walls between
...more















