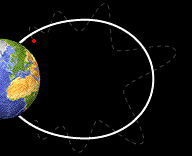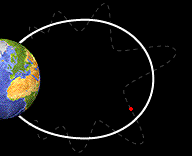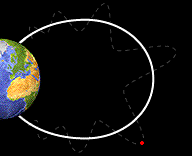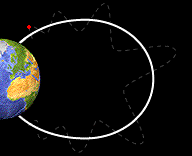
This image shows a particle bouncing back and forth from one pole of the Earth to the other.
Movie adapted from original clips provided courtesy of Professor Patricia Reiff, Rice University, Connections Program.
Basic Facts About Bounce Motion
Not only do particles spiral around magnetic field lines but they also move along the field lines toward the Earth. The crowded magnetic field lines near the poles cause particles to "reflect" and move back the same direction the from which they came. They bounce back and forth between reflection points in each hemisphere. Only a small portion of these particle penetrate into the lower atmosphere.
You might also be interested in:
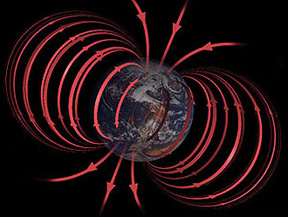
Magnetic fields can cause particles to move in these three ways: Spiral Motion Bounce Motion Drift Motion
...more
AU stands for Astronomical Units. Distances in space are too large to measure in Earth standards like miles or kilometers. For distances too large to measue in AU, we use light years. A light year is the
...more
The solar wind is formed as the Sun's topmost layer blows off into space carrying with it magnetic fields still attached to the Sun. Gusts and disturbances form in the solar wind associated with violent
...more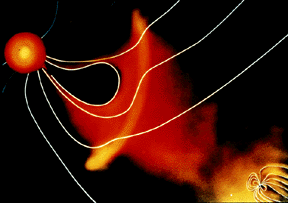
For a planet to be affected by a blob of material being ejected by the sun, the planet must be in the path of the blob, as shown in this picture. The Earth and its magnetosphere are shown in the bottom
...more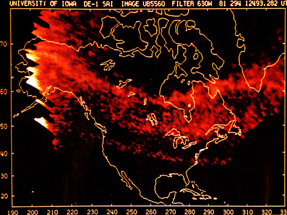
The aurora we are most familiar with is the polar aurora. This is what people are referring to when they speak of the northern or southern lights. But there are other less-known auroral activity, such
...more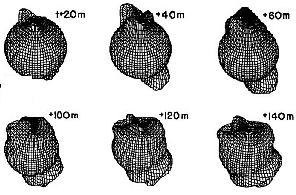
This figure shows the effect of the aurora on the atmosphere. When FAC's enter the atmosphere and create the aurora, they warm the atmosphere impulsively. This impulse travels throughout the atmosphere
...more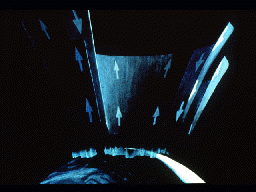
This picture illustrates the streaming of particles into and out of the auroral zone, as Field-aligned currents (FAC's) short-circuit through the ionosphere. Some of the particles entering the auroral
...more