This image shows a pool ball floating on liquid mercury. A pool ball is fairly heavy for its size, but you can see it floats on, or is less dense, than liquid mercury.
Click on image for full size
Density Definition Page
Density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given unit volume (density = mass/volume). Put simply, if
mass is a measure of how much ‘stuff’ there is in an object, density is a measure of how tightly that ‘stuff’ is packed together.
One way to see how density affects things is to look at how things float or sink in water. If something is more dense than water, it will sink, and if it is less dense it will float. This is why an anchor (very dense) sinks, but an inner tube (not very dense) floats.
You might also be interested in:

Would it be more difficult to pull an elephant or a mouse? If you pulled each animal the same amount, the mouse would come towards you but the elephant would not move at all, even if he didn’t try to
...more
The elements in the periodic table on the left are divided into three groups. The elements in the table that have green squares are called metals. Most elements are metals. They are usually shiny, seem
...more
Icebergs are large pieces of ice that are floating in the ocean. They broke off of ice shelves or glaciers in Earth’s polar regions. Icebergs are a part of the cryosphere. Almost all of an iceberg is below
...more
Solid is one of the four common states of matter. The three others are gas, liquid, and plasma. There are also some other exotic states of matter that have been discovered in recent years. Unlike liquids
...more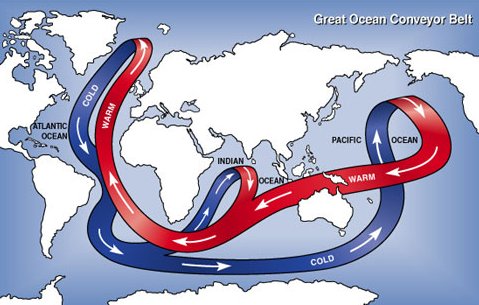
Seawater moves through the Atlantic as part of the Global Ocean Conveyor. That’s the way that seawater travels the world’s oceans. The water in the Global Ocean Conveyor moves around because of differences
...more
AU stands for Astronomical Units. It is an easy way to measure large distances in space. It is the distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is about 93 million miles. For really big distances, we
...more
The solar wind is formed as the Sun's top layer blows off into space. It carries magnetic fields still attached to the Sun. Streams appear to flow into space as if they are spiraling out from the Sun,
...more















