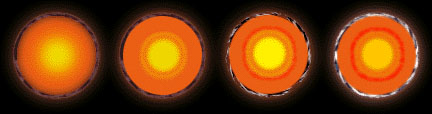
This image shows stages in the evolution of Ganymede.
Evolution of Ganymede
The moons and planets formed by accretion of rocky material and volatiles out of the primitive solar nebula. As they finished forming, about 4 Billion Years ago, the surface continued to be bombarde
d by the remmanent of planetary material available nearby. This period is called the Period of Late, Heavy Bombardment. From the Period of Late, Heavy Bombardment forward, this is probably what happened to Ganymede:
- warming and differentiation
- rapid cooling of the interior of Ganymede
- further warming and volcanism later in it's history, somewhat like case of Mars, which caused surface extension and deformation, and created the grooved ter
rain.
You might also be interested in:
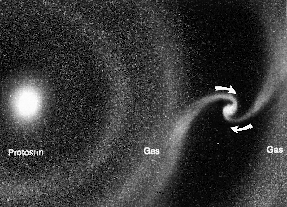
As shown in this picture, while they were forming in the solar nebula, the nucleii of the planets-to-be (called protoplanets) drew material to themselves from the cloud of gas and dust around them. The
...more
Differentiation is a scientific term which really means "to separate". In their earliest history, elements which comprised the planets and moons would part into separate regions, if the body was warm enough.
...more
This image shows an example of the grooved terrain of Ganymede. The image clearly shows that some things hit Ganymede and made craters after the grooves were made, because the grooves are underneath the
...more
Most of the moons and planets formed by accretion of rocky material and volatiles out of the primitive solar nebula and soon thereafter they differentiated. Measurements by the Galileo spacecraft have
...more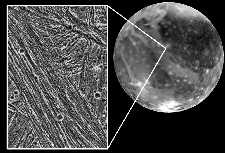
Instead of icy-volcanism, the surface of Ganymede reveals a gradual surface deformation remeniscent of the crustal deformation of the Earth. In this case, crustal extension of the surface of Ganymede resulted
...more
The diagram to the left shows a cutaway of the possible interior structure of Ganymede, based on recent measurements by the Galileo spacecraft. It shows a small core of metal, overlain with some rocky
...more
The surface of Ganymede is halfway between that of Callisto and that of Europa. Portions of the crust are of ancient age, while other portions are relatively new. The little white dots shown in this image
...more