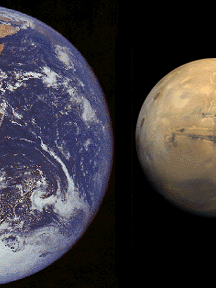
This image shows the Earth and Mars
NASA
An Overview of the History of Mars
This is probably what happened to Mars:
- an early warm period
- the inside of Mars cools off very fast
- volcanoes appeared, and the Tharsis Bulge is created
- changes in climate every once and awhile, which affect the way in which the frozen water of Mars comes to the surface.
The changes in climate may persist to the present day, but the rest of the history of Mars was finished 3.5 Billion Years ago.
The reason that the history of Mars is this way has to do with the fact that Mars is small, and the fact that Mars is farther from the sun that either the Earth or Venus. Some scientists call this the "Goldilocks" phenomenon.
You might also be interested in:

What types of instructional experiences help K-8 students learn science with understanding? What do science educators teachers, teacher leaders, science specialists, professional development staff, curriculum designers, school administrators need to know to create and support such experiences?
...more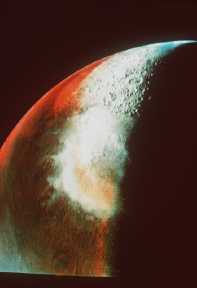
The terrestrial planets formed about 4 Billion Years ago. As the process which formed them came to an end, the planets may have been left in either of the following two states: very warm, with a softer
...more
Mars is small. Mars is about 1/3 the size of the Earth. This means that it cooled off very fast. Mars probably started colder than the other earth-like planets. Then, Mars cooled rapidly from the outside,
...more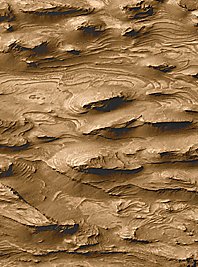
The Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) was launched on November 7, 1996. It has been in orbit around Mars for over 1500 days. It may have made its greatest observation this month! Pictures taken by the camera
...more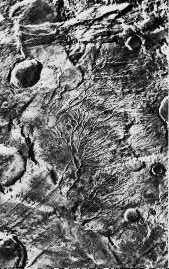
There seems to be no running water on the surface of Mars today even though there is evidence for running water, including river channels such as those shown here, and there are frozen, icy polar caps.
...more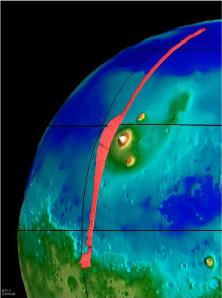
This image, taken from the Mars Global Surveyor mission (MGS), shows the Tharsis Ridge, the green/blue area in the middle of the picture, as well as a portion of the southern hemisphere of Mars. The green
...more
High resolution images returned by the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft allow closer examination of this unusual canyon. As shown here, slopes seem to descend steeply to the north and south in broad, debris-filled
...more
This view of Valles Marineris shows debris-filled gullies with intervening rocky spurs, reminiscent of terrestrial canyons. Layered rocks on Earth form from sedimentary processes (such as those that formed
...more