This is a composite image of the small moons of Saturn.
Click on image for full size
NASA
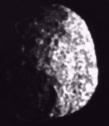
Epimetheus
Epimetheus was discovered by R. Walker in 1966. Epimetheus is the 4th closest moon to Saturn, with a standoff distance of 151,422 km. Epimetheus is one of the
small moons, being 70 x 50 km (45 x 33 miles) in size. Its dimensions make Epimetheus about the size of the city of Los Angeles.
Epimetheus and Janus orbit Saturn together. They are only 50 km (33 miles) apart as they orbit Saturn, which is a little like having two moons in the same city. The fact that they are so close may mean that they are two pieces of what may once have been a single moon.
As a small moon, the composition and surface features of Epimetheus are unknown.
You might also be interested in:
The small moons are too small to be seen, so not much is known about their surface features or composition. With no knowledge of the composition, and no clues from the surface, little can be determined
...more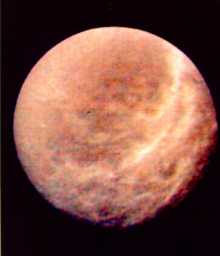
Saturn has // Call the moon count function defined in the document head print_moon_count('saturn'); moons and a complex ring system. The moon Titan is one of the few moons in the solar system with a significant
...more
This is an image of the Earth's moon, shown in the lower left, with the six much smaller icy moons of Saturn. The moons in order, starting from the top left are: Mimas, Enceladus, Tethys, Dione, Rhea,
...more
Dione was discovered by G. Cassini in 1684. Dione is the 7th farthest moon from Saturn, with a standoff distance of 377,400 km. It is a small icy moon, lightly cratered, with wispy white streaks across
...more
The surface of Dione does not have many craters, which is an indication of changes to the surface in the past. Instead it has wispy white streaks similar to those found on Rhea extending for many kilometers
...more
The surface of Enceladus does not have many craters. Instead it has grooves similar to those found on Ganymede. These grooves extend for many kilometers over the surface. The presence of grooves indicates
...more
Helene was discovered on February 29, 1980, by Pierre Laques and Raymond Despiau of the Pic du Midi Observatory, France, and J. Lecacheux from the Meudon Observatory, France. Their discovery was made using
...more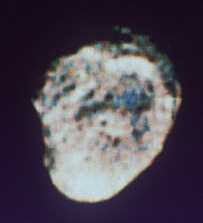
Hyperion was discovered by W. Bond in 1848. Hyperion is the 3rd farthest moon from Saturn, with a standoff distance of 1,481,000 km. Hyperion is 175 x 100 km (117 x 67 miles) in size. Its dimensions make
...more














