The Kepler mission will search for habitable planets, and determine their absolute sizes using stellar seismology.
Click on image for full size
NASA
Kepler Mission - a search for habitable planets
In March 2009, NASA launched the Kepler satellite. This
mission is designed to discover habitable Earth-like
planets around
distant Sun-like stars. The satellite has a 0.95-m telescope with an array
of digital cameras to monitor the brightness of more than
100,000 solar-type stars
for 4-6 years.
Some of the expected planetary systems will be oriented so that the
planets might pass in front of the host star. This will cause a brief
decrease in the amount of light recorded by the satellite. The duration
and depth of such a "transit" tells us about the size of the planet
relative to the star.
In general, we will not know the size of the star. So, there will be a
revolving selection of 512 stars monitored more frequently to detect
pulsations. This will provide the absolute size of the star, and thus any
planets.
You might also be interested in:

I am Katrien, a Belgian astronomer. I have been working in several European countries and I am currently based in Paris, France. My research is very exciting as I study stars that pulsate! This means
...more
Hi from McDonald Observatory in Texas! From the Lone Star State I am observing several dozen targets of the Kepler space mission. All the stars are asteroseismic targets, which means that they show stellar
...more
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was one of the most important exploration tools of the past two decades, and will continue to serve as a great resource well into the new millennium. The HST is credited
...more
Driven by a recent surge in space research, the Apollo program hoped to add to the accomplishments of the Lunar Orbiter and Surveyor missions of the late 1960's. Apollo 11 was the first mission to succeed
...more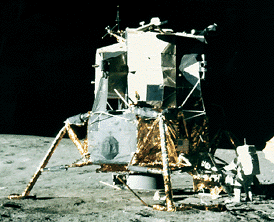
Apollo 12 survived a lightning strike during its launch on Nov. 14, 1969, and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended to the surface, while Richard Gordon
...more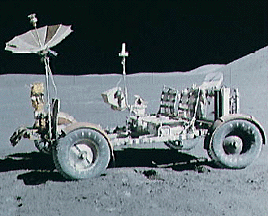
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon
...more
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program on July 7, 1999. In May 2001, Deep Impact was given the "go" from NASA to start with mission development. Deep Impact
...more















