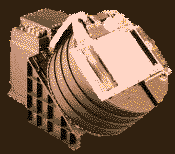
The SWOOPS ion spectrometer
Los Alamos National Laboratory
SWOOPS Instrument Page
SWOOPS stands for "Solar Wind Observations Over the Poles of the Sun". This experiment onboard
Ulysses is basically making a map of the solar plasma within
the heliosphere.
This plasma that flows from the Sun is often called the
solar wind.
You see, the SWOOPS experiment measured the solar plasma as Ulysses flew past Jupiter and it is measuring the
solar plasma in its special orbit around the Sun. This will give us the best 3-D map of the solar plasma (solar wind) within heliosphere that we have ever had!
SWOOPS is actually made up of two instruments,
the ion spectrometer and the electron spectrometer. The ion spectrometer measures the
positive ions within the solar wind and the electron spectrometer measures the electrons within the solar wind.
SWOOPS measurements determine the speed, direction, temperature and density of the solar wind flow.
The most important contribution from SWOOPS is that this instrument is helping us to map the solar wind flow throughout the heliosphere. Disturbances in the solar wind can produce space weather storms that can affect our satellites and our life on
Earth. In order to better understand and predict these space weather events, we need to
understand the Earth's surroundings. SWOOPS is helping us do just that.
You might also be interested in:

Plasma is known as the fourth state of matter. The other three states are solid, liquid and gas.In most cases, matter on Earth has electrons that orbit around the atom's nucleus. The negatively charged
...more
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was one of the most important exploration tools of the past two decades, and will continue to serve as a great resource well into the new millennium. The HST found numerous
...more
Driven by a recent surge in space research, the Apollo program hoped to add to the accomplishments of the Lunar Orbiter and Surveyor missions of the late 1960's. Apollo 11 was the name of the first mission
...more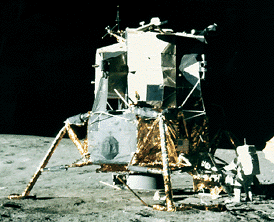
Apollo 12 was launched on Nov. 14, 1969, surviving a lightning strike which temporarily shut down many systems, and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended
...more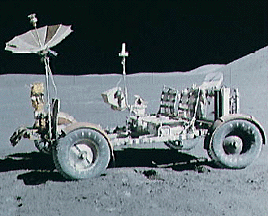
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon
...more
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program on July 7, 1999. The Discovery program specializes in low-cost, scientific projects. In May 2001, Deep Impact was given
...more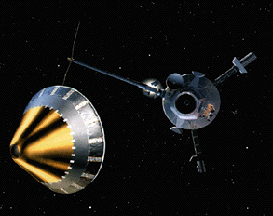
The Galileo spacecraft was launched on October 19, 1989. Galileo had two parts: an orbiter and a descent probe that parachuted into Jupiter's atmosphere. Galileo's main mission was to explore Jupiter and
...more