NASA
What is Space Weather?
Weather on Earth is the set of ever-changing ambient conditions in our atmosphere. Its elements include temperature, air pressure, wind speed and direction, humidity, precipitation, and so on. Space weather is the set of ever-changing ambient conditions in the space within our Solar System. Its elements include electromagnetic radiation, the solar wind of charged particles which flows outward from the Sun, and the force of the Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) which spirals outward from our parent star.
Space Weather Starts at the Sun
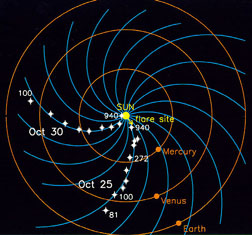
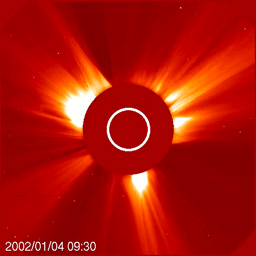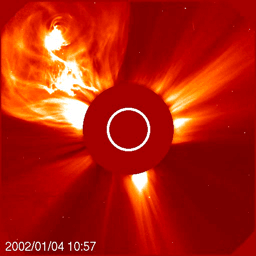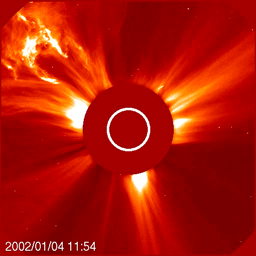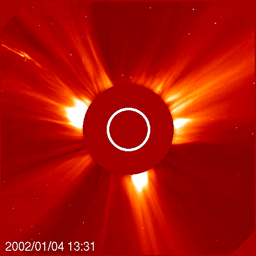
The Sun is the primary driver of space weather. Storms on the Sun, in the form of solar flares and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), can launch showers of radiation and powerful magnetic fields into interplanetary space. We are most concerned about local impacts of space weather, meaning those storms which are directed at Earth and influence our home planet.
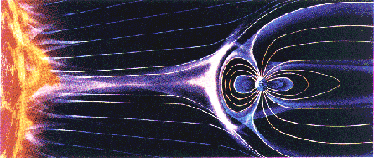
Space Weather at Earth and in Near-Earth Space (Geospace)
When a cold front on Earth encounters a mountain range the local weather conditions are influenced by the local topography. Similarly, when a strong pulse in the solar wind generated by a CME encounters Earth's magnetic field, the solar wind and Earth's magnetosphere interact in complex ways to influence the net results of the "storm" on Earth and in near-Earth space.
Short-term and Long-term Changes in Space Weather
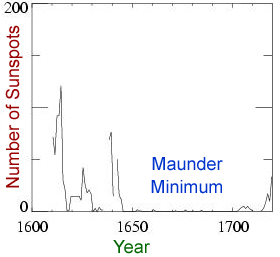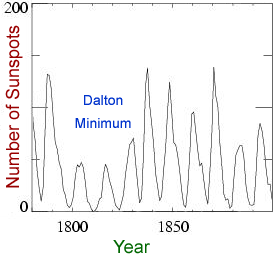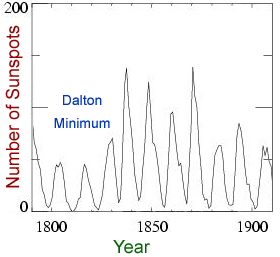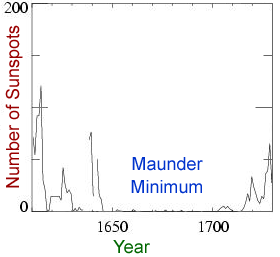
Some of our space weather comes as short-lived storms which can last minutes to hours to days. The Sun also undergoes cycles in its level of activity that span years to decades, causing longer-term variations in space weather. Finally, the Sun has changed substantially over the multi-billion year history of our Solar System, producing long term "climate change" effects in our space weather.
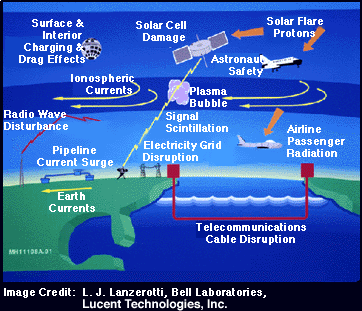
How does Space Weather affect People and Human Society?
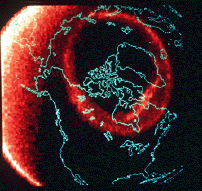
Why is space weather of interest to humans? Since sunlight is the primary driver of Earth's weather, variations in the Sun's output may influence weather and climate on Earth. Radiation from space weather storms can endanger astronauts and can damage and destroy satellites, such as those used for cell phone communications. Some electrical power grids have been knocked out of commission by especially powerful solar storms. Such storms can be sources of beauty as well as destruction. The marvelous displays of the aurora (the Northern and Southern Lights) are caused by collisions of particles energized by solar storms with gases in Earth's upper atmosphere.