Click on image for full size
Windows to the Universe original image
Related links:
Pegasus
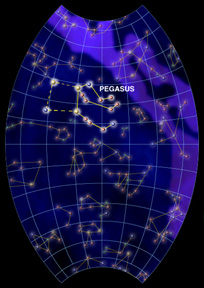
The constellation Pegasus represents the white, winged horse of Greek mythology. This beautiful figure can be seen high in the sky starting near the end of summer and continuing through autumn if you live in the Northern Hemisphere. If you are below the Equator, look for Pegasus in late winter and through spring. When looking at the image, it is difficult to see the figure as a horse. That is because the constellation is actually upside-down! Imagine it flipped over, and you can see what could be the neck and head of a horse and two legs sticking out from the famous "Square of Pegasus".
This square represents the front half of the horse's body. Mythologists are still not sure what happened to the other half of the constellation, but some believe a part of Pegasus was used to create the image of Aries the Ram. The square is very easy to find in the night sky. The neck and legs of the horse shine brightly on clear nights.
The story behind Pegasus begins with the battle between Perseus and Medusa. When Perseus severed Medusa's head, drops of blood fell into the sea. They mixed with sea foam, and Pegasus was born. The white sea foam gave the horse his brilliant color. Pegasus became friends with the warrior, Bellerophon. One day, Bellerophon tried to ride Pegasus to Mount Olympus. This angered Zeus so much that he sent a gadfly to bite Pegasus. When the horse was stung, Bellerophon fell to the Earth. Pegasus made it to the home of the gods, where he still remains.
Pegasus is home to the globular cluster, M15. This is a great object to view with a telescope because it is one of the brightest in the sky. M15 lies slightly northwest of the head, which is made of the star, Enif. Approximately one dozen galaxies are within Pegasus, the brightest one being NGC 7331. It is located just north of the "knees" of Pegasus.