Dropsondes carry instruments that measure temperature, humidity, air pressure, and wind speed. They are dropped on small parachutes from airplanes.
Image courtesy of UCAR.
Instruments in the VOCALS Field Campaign
Scientists use lots of instruments during the VOCALS field campaign. The instruments collect data about the atmosphere and the ocean. Some of the instruments are on satellites or airplanes. Other instruments are on ships or buoys in the ocean.
Radar is used to measure wind speed and to spot rainfall. It can also measure the sizes of water droplets in clouds and drizzle. LIDAR is like radar but uses laser light instead of radio waves. LIDAR measures aerosol particles and the "edges" of clouds.
Radiosondes and dropsondes are lifted into the sky on balloons or dropped on parachutes from aircraft. They carry instruments for measuring pressure, altitude, temperature, humidity, and wind speed and direction.
Cameras on aircraft and satellites take pictures of clouds and the sea surface. Radiometers measure the amount of sunlight reflected from the tops of clouds. They also measure infrared radiation coming from different levels in clouds and the atmosphere and how much light can pass through clouds. Spectrometers measure chemicals in the atmosphere and in aerosols.
Instruments towed by ship measure temperature, saltiness, pressure, and chlorophyll content in the ocean. A special kind of sonar collects data on the speed and direction of ocean currents.
You might also be interested in:

What if you wanted to learn more about the climate of a very large area of the world? What would be involved in studying how the oceans, land, and atmosphere interact? You would need to have a team of
...more
Scientists use lots of data from satellites in the VOCALS field campaign. They also gather data from instruments on ships and on airplanes. When they combine data from satellites, ships, and aircraft,
...more
Rain is precipitation that falls to the Earth in drops of 5mm or more in diameter according to the US National Weather Service. Virga is rain that evaporates before reaching the ground. Raindrops form
...more
A cloud is composed of tiny water droplets or ice crystals that are suspended in the air. A series of processes have to happen in order for these water droplets or ice crystals to form into clouds in the
...more
Drizzle is light precipitation that is made up of liquid water drops that are smaller than rain drops. Drizzle can be so light that only a millimeter of water falls to the Earth's surface in one day. It
...more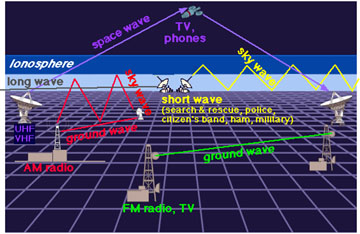
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation. A radio wave has a much longer wavelength than does visible light. We use radio waves extensively for communications. Radio waves have wavelengths as
...more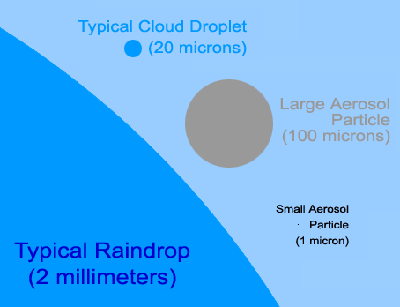
When you look up at the sky, you are looking at more than just air. There are also billions of tiny bits of solid and liquid floating in the atmosphere. Those tiny floating particles are called aerosols
...more















