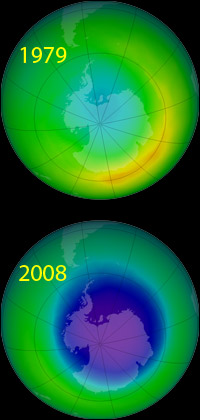
Ozone concentrations over Antarctica in October 1979 and October 2008. The ozone hole is the large purple and blue area in the 2008 image.
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy NASA.
Ozone Hole
The Ozone Hole is a major "thinning" of the ozone layer in Earth's atmosphere. It was first noticed in the late 1970s. The hole appears in the winter over the poles, especially the South Pole. Various chemicals that humans release into the atmosphere help cause the hole. Special weather patterns near the poles in winter also help cause the holes to form.
Ozone in the stratosphere protects us from ultraviolet radiation in sunlight. The ozone layer is sort of like sunscreen for planet Earth. That's why holes in the ozone layer are bad news.
Ozone is an unusual type of oxygen molecule. Normally, there are higher concentrations of ozone at various altitudes in the stratosphere. Sometimes, under the right conditions, chemical reactions in the ozone layer can destroy most of the ozone, creating an ozone "hole".
People from many countries have agreed to stop emitting most of the chemicals that destroy ozone. Scientists are hopeful that ozone holes will disappear sometime in the future if we continue to stop emissions of the problematic chemicals.
You might also be interested in:

Antarctica, home to the South Pole, is very cold! In fact, Antarctica is colder than even the Arctic! Temperatures as low as -129 degrees F (-89 degrees C) have been recorded, and in the interior, near
...more
Phenomena in the Polar Atmosphere There are some unique phenomena that happen in the atmosphere that is above the Earth's polar regions. Read on to discover more about some of the unique parts of the polar
...more
About 90% of the ozone in the Earth's atmosphere is found in the region called the stratosphere. This is the atmospheric layer between 16 and 48 kilometers (10 and 30 miles) above the Earth's surface.
...more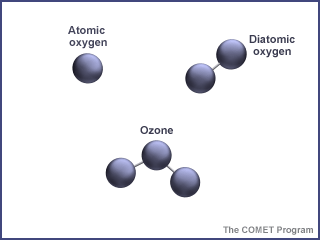
Ozone is a special kind of oxygen molecule. Normal oxygen molecules (O2), the kind we need to breathe, have two oxygen atoms. Ozone molecules (O3) have three oxygen atoms. Ozone forms when a photon of
...more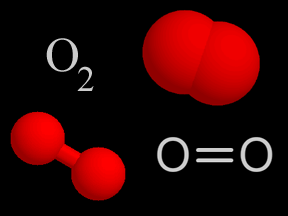
Oxygen (O2) is a kind of gas. A lot of the air you breathe is oxygen. That's a good thing, since we need oxygen to stay alive! About 4/5ths of the air in Earth's atmosphere is nitrogen (N2). Almost all
...more
What do smog, acid rain, carbon monoxide, fossil fuel exhausts, and tropospheric ozone have in common? They are all examples of air pollution. Air pollution is not new. As far back as the 13 th century,
...more
Rainbows appear in the sky when there is bright sunlight and rain. Sunlight is known as visible or white light and is actually a mixture of colors. Rainbows result from the refraction and reflection of
...more