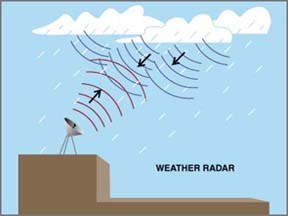
Radar bounces radio waves off water particles in clouds.
Click on image for full size
Weather Radar
Radar is important to weather forecasters because it can detect rain and hail. The radar bounces radio waves off water particles in clouds. A computer measures how long it takes for the radio waves to reflect back and then uses the time to calculate how far the particle is from the radar. It also measures how much energy is reflected back to the radar, which lets us know how much precipitation is in the clouds.
A new kind of radar called Doppler radar can do a lot more. In addition to showing how far away a raindrop is, Doppler radar can also calculate if that raindrop is moving toward or away from the radar. Meteorologists know that if the rain is moving, wind must be pushing it. This is how they know where the wind is blowing in the clouds.
You might also be interested in:

Radar is short for "radio detection and ranging". A transmitter sends pulses of high frequency radio waves. A radar echo shows up on a monitor and shows where the object is located.. A computer measures
...more
Rain is precipitation that falls to the Earth in drops of 5mm or more in diameter according to the US National Weather Service. Virga is rain that evaporates before reaching the ground. Raindrops form
...more
Wind is moving air. Warm air rises, and cool air comes in to take its place. This movement creates different pressures in the atmosphere which creates the winds around the globe. Since the Earth spins,
...more
How many hurricanes will form this year? How strong will they be? While no one can say for sure, teams of scientists make predictions each year about the strength of the upcoming hurricane season. To make
...more
Below is a list of some weather conditions that call for an advisory, watch, or warning. Severe Thunderstorm Watch: A severe thunderstorm watch is issued when a thunderstorm with winds greater than 57
...more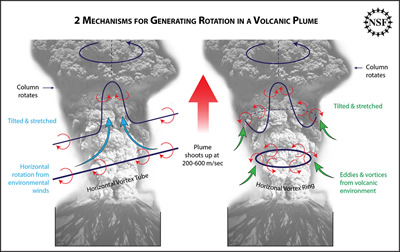
Scientists are using information they have from past volcanic eruptions to better understand strong volcanic plumes. They have observed that in some volcanic eruptions, there is a spontaneous formation
...more
Scientists sometimes travel in specially outfitted airplanes in order to gather data about atmospheric conditions. These research aircraft have special inlet ports that bring air from the outside into
...more