Click on image for full size
Windows Original (Original map is from Wikipedia Commons)
Related links:
Motions of the Ocean - An Overview
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute: Beaufort Gyre
Wikipedia's Great Pacific Garbage patch
Changing Planet: The Case of the Leaky Gyre
Changing Planet Navigation Page
Researching under the Arctic Sea Ice
Resources for Teaching about the Poles and the Cryosphere
Ocean Gyres
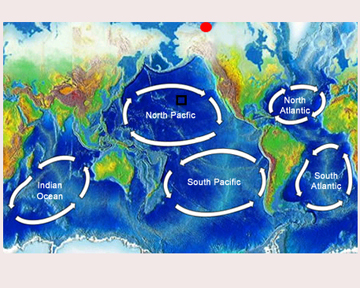
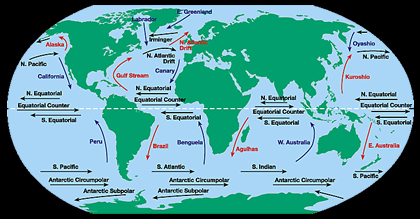
Have you ever played with a toy called a gyroscope? It spins around and around. Scientists use the similar word gyre to explain something that moves in a circle. There are gyres in the ocean that are huge swirling bodies of water. They can take up a whole ocean. In fact, the biggest ocean gyres are named for the oceans they are found in: North Atlantic, South Atlantic, North Pacific, South Pacific and Indian Ocean gyres. A simple drawing of those can be seen on this page.One of the biggest ocean gyres, the North Pacific gyre, is home to an area called the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. This area contains a lot of litter! It covers an area about twice the size of Texas and contains about 3 million tons of plastic litter.
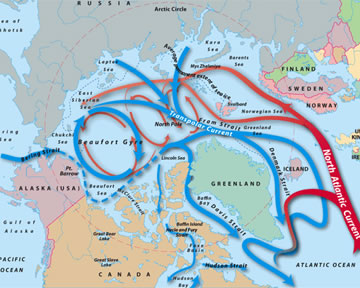
There are smaller gyres in the ocean too. One of the smaller gyres is called the Beaufort gyre and it is in the Arctic Ocean. Scientists have been studying the Beaufort gyre a lot recently because it could actually impact the climate (long-term weather patterns) in North American and Western Europe.
Ocean gyres are currents on the top of the ocean that are driven by the winds of the Earth. Ocean gyres in the Northern hemisphere rotate clockwise and gyres in the Southern hemisphere rotate counter-clockwise.