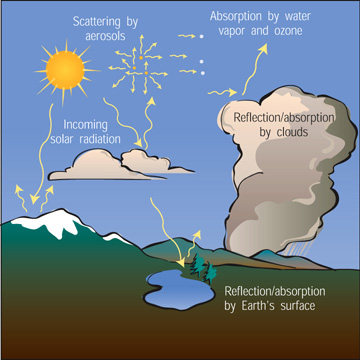
This picture shows what happens to energy from the Sun once it gets to Earth.
Click on image for full size
NCAR
When Energy Gets to Earth:
Once energy from the Sun gets to Earth, several things can happen to it:
- Energy can be scattered or absorbed by aerosols in the atmosphere. Aerosols
are dust, soot, sulfates and nitric oxides. When aerosols absorb energy,
the atmosphere becomes warmer. When aerosols scatter energy, the atmosphere
is cooled.
- Short wavelengths are absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere.
- Clouds may act to either reflect energy out to space or absorb energy,
trapping it in the atmosphere.
- The land and water at Earth's surface may act to either reflect energy
or absorb it. Light colored surfaces are more likely to reflect sunlight,
while dark surfaces typically absorb the energy, warming the planet.
Albedo is the percentage of the Sun's energy that is reflected back by
a surface. Light colored surfaces like ice have a high albedo, while dark colored
surfaces tend to have a lower albedo. The buildings and pavement in cities have
such a low albedo that cities have been called "heat islands" because
they absorb so much energy that they warm up.
Last modified July 12, 2004 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

Arctic sea ice is covered with snow all winter. Bright white, the snow-covered ice has a high albedo so it absorbs very little of the solar energy that gets to it. And during the Arctic winter, very little
...more
On spring winds, something wicked this way comes. At least for the Colorado Rocky Mountains and their ecosystems, as well as people who depend on snowmelt from these mountains as a regional source of water.
...more
Changes in the cryosphere have a considerable impact on global climate. This is because the cryosphere is an important part of the Earth system and because it is so interconnected with other parts of the
...more
“Taiga” is a Russian word meaning dense evergreen forest. The taiga biome, the largest biome on land, is full of dense evergreen forests. Located just south of the tundra in the northern parts of Europe,
...more
Energy from the Sun is one of the primary drivers of the Earth system. The Sun warms our planet, heating the surface, the oceans and the atmosphere. This energy feeds atmospheric processes and is a primary
...more
If you were fortunate to spend time recently in the Maldives, a collection of tropical islands in the central Indian Ocean, you may have seen a collection of tiny aircraft buzzing overhead. With a wingspan
...more
Precipitation falling from stratocumulus clouds changes their structure and therefore affects how much sunlight they reflect. We call this form of light precipitation drizzle. So even though there is no
...more