This is an image of Lassen Peak, in California, USA.
Click on image for full size
Image from: U.S. Geological Survey
Lassen Peak
Lassen Peak is an example of what is called a "volcanic dome".
Volcanism is thought to have begun at the center between about 600,000 and 350,000 years ago (the late Pleistocene and Holocene periods), and the eruption history continues with a lot of activity in the last 35,000 years.
The most recent eruptive activity occurred at Lassen Peak in 1914-1917. This eruptive episode
began on May 30, 1914, when a small phreatic eruption occurred at a new vent
near the summit of the peak. More than 150 explosions of various sizes
occurred during the following year. By mid-May 1915, the
eruption changed in character; lava appeared in the summit crater and
subsequently flowed about 100 m over the west and probably over the east
crater walls. Disruption of the sticky lava on the upper east side of Lassen
Peak on May 19 resulted in an avalanche of hot rock onto a snowfield. A
lahar was generated that reached more than 18 km down Lost Creek. Intermittent eruptions of variable intensity continued until about the middle of 1917.
You might also be interested in:

Ash is made of millions of tiny fragments of rock and glass formed during a volcanic eruption. Volcanic ash particles are less than 2 mm in size and can be much smaller. Volcanic ash forms in several ways
...more
Cinder cones are simple volcanoes which have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit and rarely rise more than a thousand feet above their surroundings. They usually are created of eruptions from a single vent,
...more
Lava can move in broad flat lava flows, or it can move through constrictive channels or tubes. Lava flows have a large surface area so they tend to cool quickly and flow slowly. The fastest unconstricted
...more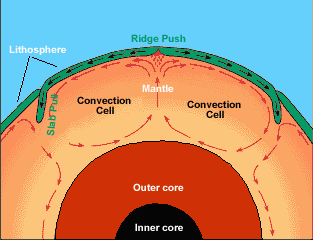
Earth’s center, or core, is very hot, about 9000 degrees F. This heat causes molten rock deep within the mantle layer to move. Warm material rises, cools, and eventually sinks down. As the cool material
...more
Many kinds of surface features provide evidence of a sliding lithosphere. When two plates move apart, rising material from the mantle pushes the lithosphere aside. Two types of features can form when
...more
Magma consists of remelted material from Earth's crust and fresh material from the aesthenosphere, relatively near the Earth's surface. When magma is erupted onto the surface in the form of lava, it becomes
...more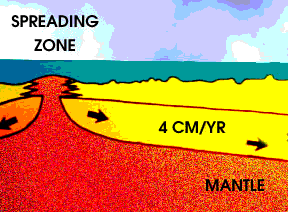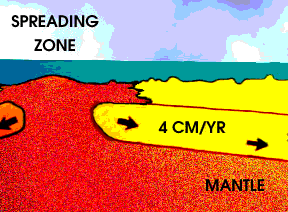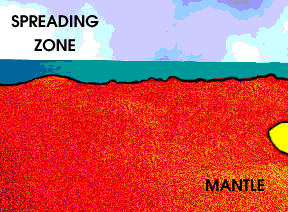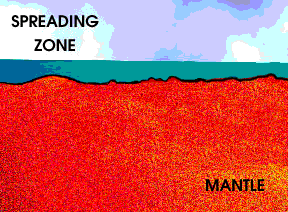
As the Earth cools, hot material from the deep interior rises to the surface. Hot material is depicted in red in this drawing, under an ocean shown in blue green. The hotter material elevates the nearby
...more















