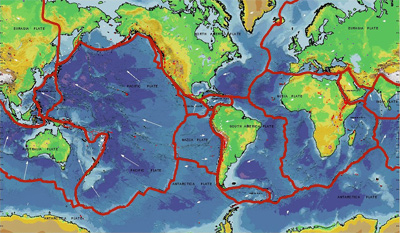
A map of Earth's tectonic plates. Plate boundaries are shown in red. Learn more about the geologic features related to Earth's tectonic plates at
This Dynamic Planet.
Click on image for full size
Modified from USGS
Plate Tectonics
Many forces cause the surface of the Earth to change over time. However, the largest force that changes our planet's surface is the movement of Earth's outer layer through the process of plate tectonics. This process causes mountains to push higher and oceans to grow wider.
As shown in this diagram, the rigid outer layer of the Earth, called the lithosphere, is made of plates which fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. These solid but lightweight plates seem to "float" on top of a more dense, fluid layer underneath.
Motions deep within the Earth carry heat from the hot interior to the cooler surface. These motions of material under the Earth's surface cause the plates to move very slowly across the surface of the Earth, at a rate of about 2 inches per year. There are several different hypotheses to explain exactly how these motions allow plates to move.
Interesting things happen at the edges of plates. Subduction zones form when plates crash into each other, spreading ridges form when plates pull away from each other, and large faults form when plates slide past each other.
You might also be interested in:

Many kinds of surface features provide evidence of a sliding lithosphere. When two plates move apart, rising material from the mantle pushes the lithosphere aside. Two types of features can form when
...more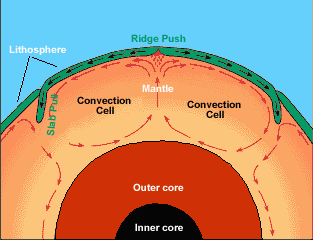
Earth’s center, or core, is very hot, about 9000 degrees F. This heat causes molten rock deep within the mantle layer to move. Warm material rises, cools, and eventually sinks down. As the cool material
...more
When two sections of the Earth's lithosphere collide one slab of lithosphere can be forced back down into the deeper regions of the Earth, as shown in this diagram. This process is called subduction.
...more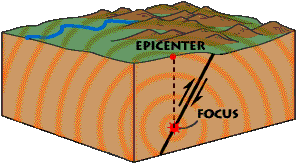
The expression "on solid ground" is often used to describe something as stable. But sometimes the solid ground underfoot is not stable. It moves as Earth's tectonic plates move. Sometimes it moves gradually.
...more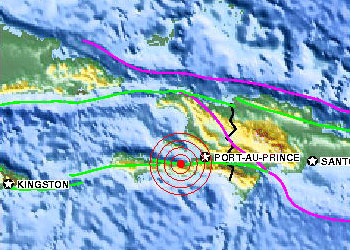
A major earthquake causing widespread devestation and extensive loss of life struck the nation of Haiti on January 12, 2010. The earthquake had a magnitude of 7.0. Haiti is on the island of Hispaniola
...more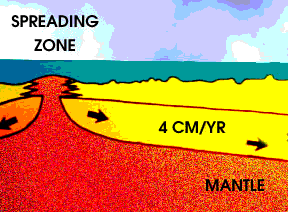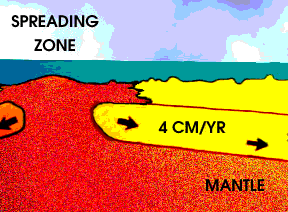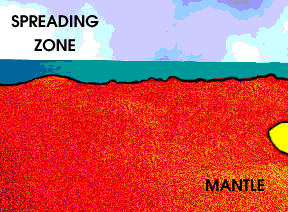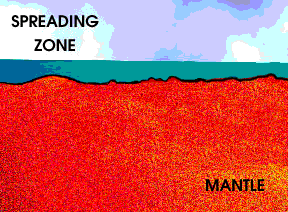
As the Earth cools, hot material from the deep interior rises to the surface. Hot material is depicted in red in this drawing, under an ocean shown in blue green. The hotter material elevates the nearby
...more
Mountains are built through a general process called "deformation" of the crust of the Earth. One example of deformation comes from the process of subduction. When two sections of the Earth's lithosphere
...more