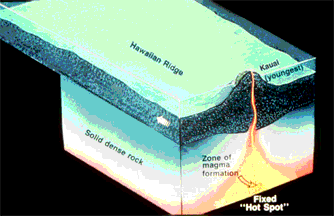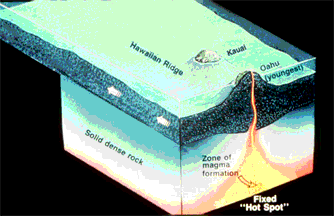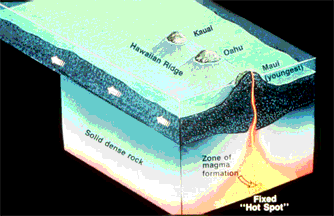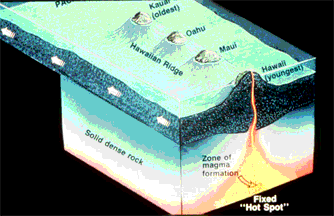
This is a drawing of how a hot spot under the crust builds land on the surface.
Click on image for full size
Image copyright 1997 by the American Geophysical Union. Further electronic distribution is not allowed.
Plume Volcanism
The Hawaiian Islands are an example of the way some volcanoes are made. A rising hot bubble of material finds it's way into the crust of the Earth from the deep interior, and erupts material unto the surface. This bubble or "plume" is called a "hot spot". Lava from the eruption turns to layers of rock and builds a volcanic "cone". Continual eruptions eventually build a whole island on the surface.
On Earth, the hot spot is still, and the portion of crust on which the islands are formed moves past the hot spot. In this drawing, the crustal plate moves to the left, past the stationary hot spot or plume. Each island which is created has a volcano associated with it. The oldest island is at the upper left, the youngest at the lower right. This way, a chain of islands are formed, each one younger than the last. The oldest islands wear down by erosion, become covered by ocean water, and eventually return to the sea.
A similar process built the Tharsis Ridge of Mars and many volcanic rises on Venus. On these planets, the crust did not move past the hot spot, but stayed in place. The volcanoes of Mars which were built this way became *very* large indeed.
You might also be interested in:

Volcanoes form when hot material from below risesand leaks into the crust. This hot material, called magma, comes either from a melt of subducted crustal material, and which is light and buoyant after
...more
Ash is made of millions of tiny fragments of rock and glass formed during a volcanic eruption. Volcanic ash particles are less than 2 mm in size and can be much smaller. Volcanic ash forms in several ways
...more
Cinder cones are simple volcanoes which have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit and only grow to about a thousand feet, the size of a hill. They usually are created of eruptions from a single opening,
...more
Lava can move in broad flat lava flows, or it can move through tight channels or tubes. Lava flows tend to cool quickly and flow slowly. The fastest lava outside of channels moves at about 6 mi/hr an easy
...more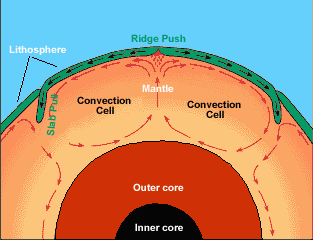
Plates at our planet’s surface move because of the intense heat in the Earth’s core that causes molten rock in the mantle layer to move. It moves in a pattern called a convection cell that forms when
...more
Many kinds of surface features are clues that our lithosphere is sliding. Two types of features can form when plates move apart. At mid ocean ridges, the bottom of the sea splits apart and new crust is
...more
Magma consists of remelted material from Earth's crust and fresh material from other regions near the Earth's surface. When magma is erupted onto the surface in the form of lava, it becomes silicate rock.
...more