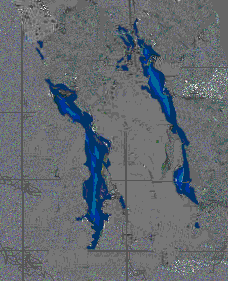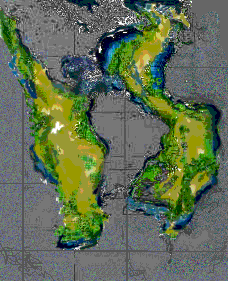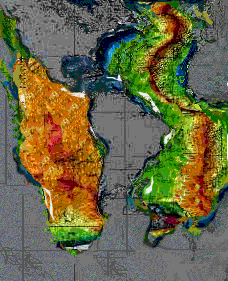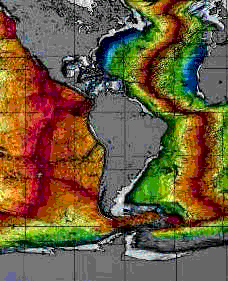
This diagram shows the Americas being separated from the Europe and Africa as the seafloor spreads. Continents are grey in color. Youngest seafloor is red and as seafloor gets older it becomes yellow, green and then blue.
Click on image for full size
NOAA/NESDIS/National Geophysical Data Center, Boulder, CO.
Seafloor Spreading
This picture explains how seafloor spreading works! It shows the ages of ocean floor in the Atlantic and eastern Pacific Oceans.
The red sections are the newest area of the seafloor. They are at mid-ocean spreading ridges. These are places at the bottom of deep oceans where there is a crack between two plates and new lava comes to the surface from deep within the Earth.
As new seafloor forms at the spreading ridges, older parts move away from the ridge. The blue areas are the oldest. Sometimes the oldest parts of the seafloor are next to land and sometimes they are near places where subduction is happening.
You might also be interested in:
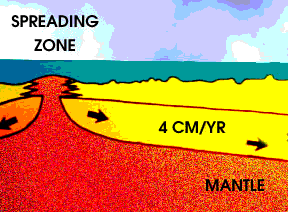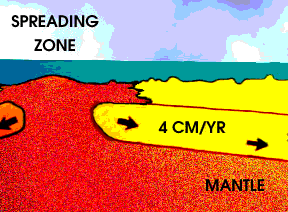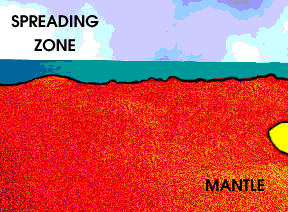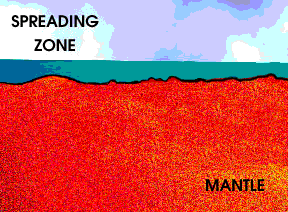
As the Earth cools, hot material from the deep interior rises to the surface. Hot material is red in this drawing, under an ocean shown in blue green. The hotter material raises the nearby layers, and
...more
When two sections of the Earth's crust collide, one slab of lithosphere can be forced back down into the deeper regions of the Earth, as shown in this picture. The slab that is forced back into the Earth
...more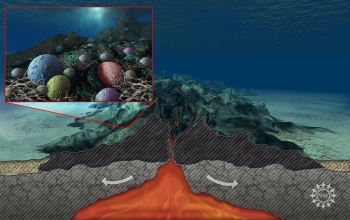
Has anyone ever told you that you shouldn’t eat things that you find on the floor? Well, the rules are different for bacteria. Scientists have found tons of bacteria at the bottom of the ocean. And it
...more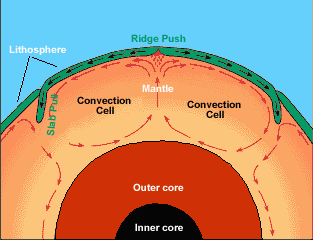
Plates at our planet’s surface move because heat in the Earth’s core causes molten rock in the mantle layer to flow. We used to think the Earth’s plates just surfed on top of the moving mantle, but now
...more
Many kinds of surface features are clues to a sliding lithosphere. Two types of features can form when plates move apart. At ocean ridges, the crust splits apart to make room for molten mantle rock. Continental
...more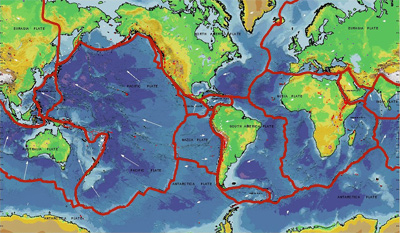
Many forces change the surface of the Earth over time. The largest force that changes our planet's surface is movement of Earth's outer layer in a process called plate tectonics. As shown in this picture,
...more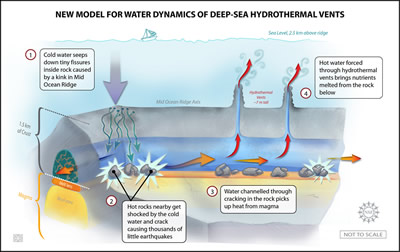
A group of scientists have been studying an area of the ocean floor called the East Pacific Rise, which is about 565 miles southwest of Acapulco, Mexico. The East Pacific Rise is a ridge along the ocean
...more