Click on image for full size
L.Gardiner/Windows to the Universe
Element (Chemical Element)
An element (also called a "chemical element") is a substance made up entirely of atoms having the same atomic number; that is, all of the atoms have the same number of protons. Hydrogen, helium, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, gold, silver, lead, and uranium are well-known examples of elements.
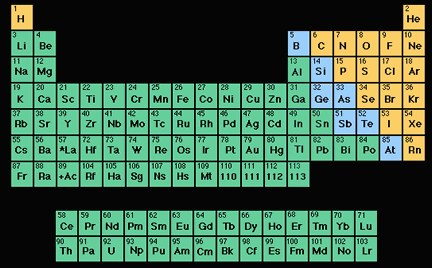
Chemists use a special type of chart, called the "periodic table", to organize the elements into groups based on similar chemical properties. There are 94 different elements that we know of which occur in nature on Earth. All of them, plus one other (californium) have been detected in space. Humans have been able to make many other new elements that don't occur in nature, usually by crashing atomic nuclei together at super high speeds in particle accelerators. As of 2007, there were 117 know elements, 22 of which were created by people.
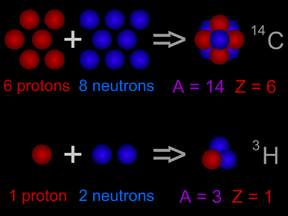
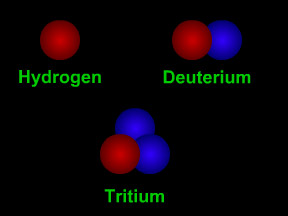
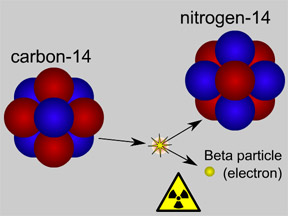
Most elements come in more than one variety. An atom of an element might have different numbers of neutrons in its nucleus. Such atoms are called "isotopes" of the element. For example, normal hydrogen has just one proton and no neutrons in its nucleus. An isotope of hydrogen called "deuterium" has one proton plus one neutron in its nucleus. A radioactive isotope of carbon is often used to figure out how old things are using a technique called "carbon dating". Most natural carbon is carbon-12 (or 12C); it has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Radioactive carbon-14 (14C) has 6 protons plus 8 neutrons. Scientists measure the ratio of 12C to 14C in objects to tell how old they are.
Hydrogen is the most common element in the Universe, followed by helium. Both formed soon after the Big Bang that gave birth to the Universe. Pretty much all of the other elements, including much of the stuff that makes up your body, were created in supernova explosions of dying stars. You are truly a "child of the Universe"! Oxygen and carbon are the third and fourth most abundant elements in the Universe. Oxygen is also the most abundant element by mass in Earth's crust, and the second most abundant gas (after nitrogen) in our planet's atmosphere.
Many common substances are made of molecules that consist of two or more different types of atoms. Since they have more than one type of atom, these substances are NOT elements; they are called compounds. Water (H2O) is probably the best-known compound; it has two different types of atoms (elements) in it, hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O). Glucose, a simple sugar, is another example of a compound. Glucose molecules (C6H12O6) have atoms of the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in them.
All of the elements have one- or two-letter abbreviations. Some are obvious, like hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), carbon (C), uranium (U), helium (He), or calcium (Ca). Some seem to make no sense at all, like lead (Pb), silver (Ag), and gold (Au). In the case of the seemingly nonsense symbols, the letters are derived from the name of the element in a language that has been used for scientific terminology throughout the ages, typically Greek or Latin. In Latin, lead (Pb) is "plumbum", silver (Ag) is "argentum", and gold (Au) is "aurum".