Interactive Animation of Seafloor Spreading and Magnetic Field Reversals
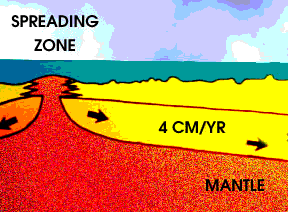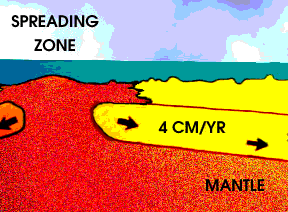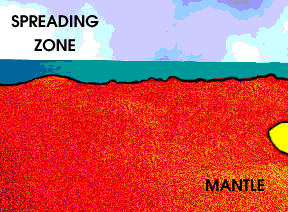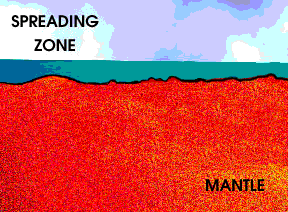
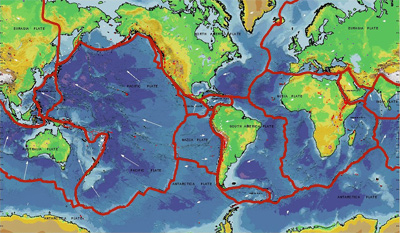
Earth's magnetic field reverses itself from time to time; North becomes South and South becomes North. Lava that cools and becomes rock at a given time in Earth's history stores a record of our planet's magnetic polarity at the time of the rock's formation. Rocks on the seafloor on either side of a mid-ocean spreading ridge preserve a record of the Earth's magnetic field over time. The discovery of this phenomenon was an important bit of evidence that helped confirm the theory of plate tectonics.
The interactive animation below illustrates this concept. Drag the compass, which represents a magnetometer, to the right and left. Can you find places where the magnetism of the rocks reverses? This section of seafloor is in the North Atlantic Ocean near Iceland. The rate of plate movement in this area is about 25 millimeters (1 inch) per year, or about 25 km (16 miles) every million years. Can you determine when the field reversals occurred?
Click the "Distance" checkbox to view a distance scale. Click the "Age" checkbox to see the age of the seafloor on either side of the ridge.
(Note: If you cannot see the animation below, or it is not working properly, you may need to download the latest Flash player.)
On this section of the seafloor, the history of Earth's magnetic field that is revealed includes the following periods:
- Brunhes normal - present time to 730 thousand years ago
- Matuyama reverse - 0.73 to 2.48 million years ago (ma)
- Gauss normal - 2.48 to 3.40 ma
- Gilbert reverse - 3.40 to 5.3 ma
If you want to build a physical model of this system, check out the seafloor spreading section of our "Magnetometer Extensions" activity.