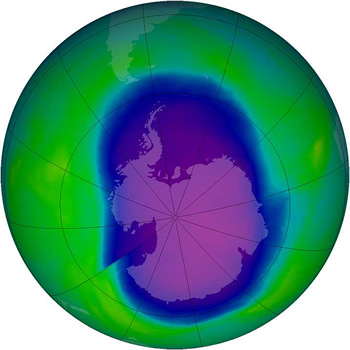
Earth's ozone hole, shown here (in blue) in 2006, could be negatively affected by some efforts to decrease climate change.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of NASA
Adding Sulfate Particles to Stratosphere Could Have Huge Impact on Earth's Ozone Layer
News story originally written on April 24, 2008
Some scientists who study the Earth's climate have been looking for ways to cool the planet because they are worried that humans aren't doing enough to prevent major changes in our climate. One idea they have is to inject particles that block the Sun into a layer of the atmosphere called the stratosphere. These particles, called sulfates, would block the Sun and cool the climate in the same way that sulfur particles from volcanoes cool the Earth after a volcanic eruption.
Unfortunately, this solution might create other big problems for our planet. A new study, headed by a scientist named Simone Tilmes, says that putting sulfates into the stratosphere would have a huge impact on the Earth's protective ozone layer. It would also make the recovery of the Antarctic ozone hole take much longer and would cause a lot of ozone loss over the Arctic region. The ozone layer is very important for life on Earth because it blocks dangerous ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
The scientists concluded that there needs to be more research done in this area before we decide that injecting sulfates into the stratosphere is a good thing for our planet.
You might also be interested in:

How do you know to pack your bathing suit and sunhat for a trip to a tropical island or pack warm sweaters and coats for a trip to Alaska? If you know a little about regional climates, then you know what
...more
Have you ever heard of ozone? That's a word that shows up in the news a lot! Do you know what ozone is and why it is important in the Earth's atmosphere? Ozone is made of three oxygen atoms (O3). You've
...more
What Will You Find There? If you travel to the South Pole, you will find the continent of Antarctica surrounded by the Southern Ocean. The geographic South Pole is marked by a large sign that scientists
...more
In the Arctic, you will find the Arctic Ocean surrounded by the continents of Europe, Asia, and North America. You will find the geographic North Pole and the magnetic North Pole there; both are in the
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. Adam Kent, a geologist at Oregon State University, says this
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core. The mantle is made up of many different reservoirs that have different chemical compositions. Scientists
...more
Some faults look strong and like they wouldn’t cause an earthquake. But it turns out that they can slip and slide like weak faults causing earthquakes. Scientists have been looking at one of these faults
...more