The Mars Observer spacecraft in the clean room.
Click on image for full size
NASA/JPL
Mars Observer
Mars Observer, also called MO for short, was sent to observe the weather, the magnetic field, and the
surface of Mars. It carried 8 different instruments.
But, MO failed on August 21, 1993. There was a fuel leak that caused the spacecraft to blow up!
NASA used what it had learned to create the successful Mars Global Surveyor mission. That just goes to show that you too can learn from your mistakes!
You might also be interested in:

The Mars Climate Orbiter was sent to the Red Planet to study its weather. It reached the planet last Thursday morning, but there was a problem. The satellite went too far into Mars' atmosphere, and burned
...more
When Mars Observer blew up, the Mars Surveyor Program was born. The Surveyor Program was suppose to consist of 8 spacecraft. The spacecraft were named: Mars Pathfinder, Mars Global Surveyor, Mars '98,
...more
The Viking I and Viking 2 missions were to both orbit Mars and land on the planet's surface. There were two spacecraft for each mission. At this stage in the history of the exploration of Mars, scientists
...more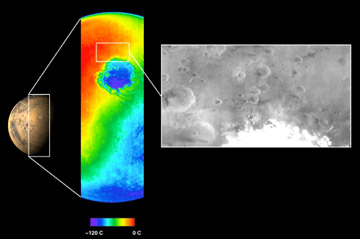
The Mars Odyssey was launched April 7, 2001. After a six-month journey, the Odyssey arrived at Mars on October 24, 2001. The instruments onboard the Mars Odyssey will study the minerals on the surface
...more
The Mars 2005 mission is still in the planning stages. It is set to launch in the year 2005.
...more
Aerobraking slowed the Mars Global Surveyor down when it reached Mars. Aerobraking also helped MGS to get into the right orbit for mapping the surface of Mars. Aerobraking means that the MGS flew through
...more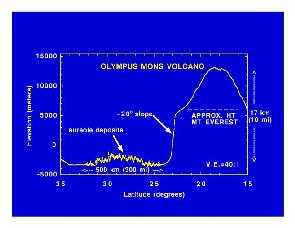
Mars Global Surveyor carries an instrument which measures the heights of things. This instrument is called an altimeter, or "altitude-meter". The graph to the left shows the results returned from Mars
...more















