A classic image of Mars from the Viking lander.
Click on image for full size
NASA/JPL
The Viking Missions
The Viking I and Viking 2 missions were designed to both orbit Mars and land and make exploratory observations on the planet's surface. At this stage in the history of the exploration of Mars, scientists had no idea what to expect nor what they might discover upon landing on the surface.
The landers verified Mariner missions' bleak findings of the "lunar-esc" Martian landscape, and performed soil studies similar to those performed by Mars Pathfinder (MPF). The soils examined by the Viking missions were found to be similar, but unlike those explored by MPF!
Immediately prior to Viking 2 orbit insertion, Mars was completely enveloped in a global dust storm, rendering the surface invisible to cameras for several months. It was the first time that scientists realized the extent and potential intensity of Martain dust storms. Eventually, pictures *were* returned by the Viking orbiters and these pictures contained valuable information about Martian channels and other surface features. Among other things, altimetry measurements from the Viking orbiters helped establish the enormous size of Olympus Mons, which was first imaged by Mariner 9. Viking made more complete measurements of the figure of Mars, measurements which help scientists understand the interior of the planet and the existence of the bulge called Tharsis Ridge.
Some of the data returned from these two spacecraft are shown in the image archive below. With this data, scientists began to make the first educated guesses about what the interior, surface history, and evolution of Mars must be.
The next American spacecraft to scheduled visit Mars was the Mars Observer mission.
You might also be interested in:

How did life evolve on Earth? The answer to this question can help us understand our past and prepare for our future. Although evolution provides credible and reliable answers, polls show that many people turn away from science, seeking other explanations with which they are more comfortable.
...more
The Viking missions to Mars were part of a series of U.S. efforts to explore and better understand the red planet. Each Viking spacecraft consisted of an orbiter and lander. The landers were sterilized
...more
Soils form through a complex interaction of the molecules of soil with particles and molecules of the atmosphere. Measurements of the soil contribute to an understanding of a planet's climate, weather,
...more
This image shows a local dust storm near the edge of the south polar cap. Viewing of this image at high resolution is recommended. This fascinating image shows dust swirling over a large area. Martian
...more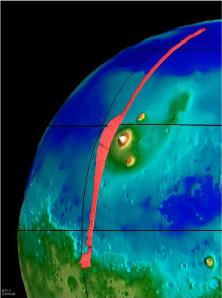
This image, taken from the Mars Global Surveyor mission (MGS), shows the Tharsis Ridge, the green/blue area in the middle of the picture, as well as a portion of the southern hemisphere of Mars. The green
...more
The Mars Observer set out to observe the atmosphere (detailed weather rather than climate), magnetic field and surface of Mars. It carried with it 8 instruments. However, the Mars Observer (MO) failed
...more
In spite of Mars' similarity to Earth in size and proximity to the sun, the environment of Mars seems unfriendly toward life as we know it on Earth. Mars is small, so there is not much gravity. For this
...more
In spite of the fact that Mars has an atmosphere, the environment of Mars seems unfriendly toward life as we know it on earth. Mars is small, so there is not much gravity. For this reason, much of the
...more













