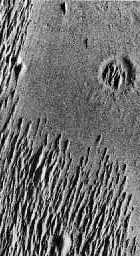
This image shows some of the dunefields of Mars.
Click on image for full size
NASA
Martian Dunefields
This is an example of Martian sand dunes. They are found in the southern hemisphere. They show that wind can change the surface of a planet. Wind is very important to the erosion of the Martian landscape.
Sand dunes were also seen at equatorial latitudes by Mars Pathfinder and also by the Viking I lander in the Chryse Planitia Basin (check the large topographic map of Mars for the distances between these two landing sites).
You might also be interested in:

Unlike the rocks of Earth, where there are many things which cause erosion, the rocks of Mars erode because of only two things: wind and acid fog. Acid fog is very important, but because there is not a
...more
During the Mars Pathfinder Rover's exploration of the Martian surface, it went over what scientists now call the "Mermaid Dune". The soil on top of Mermaid Dune seemed to be dark gray. However, when the
...more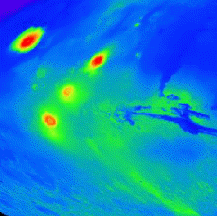
On this map of Mars, the lightly cratered Tharsis Ridge is shown, as well as the heavily cratered Martian highlands (near the bottom of the picture), and Valles Marineris to the right. The volcanoes are
...more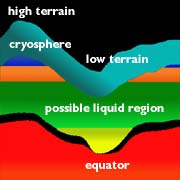
On Mars, the water is trapped, frozen, within the ground. Nevertheless, there is evidence for running water on Mars. When the water is melted and released to the surface, it will run from higher ground
...more
The drawing shows the depth at which water may be frozen into the ground. To have water running on the surface of Mars, this water region must be near to the surface. This may have happened at various
...more
Separate from the Martian outflow channels, or the river valleys, are large Martian lakes (600 km, or ~1000 miles across) which once were part of a flood.
...more
This picture shows fog on Mars. More fog has been seen in images returned by Mars Global Surveyor of the south polar region of Mars. Martian fog may have a little bit of acid mixed in with the water drops.
...more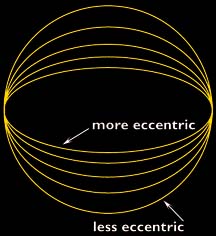
The orbit of Mars is very oval shaped. The orbit is much more oval shaped than the Earth's orbit. This means that the climate of Mars can change drastically between warm and cold.
...more