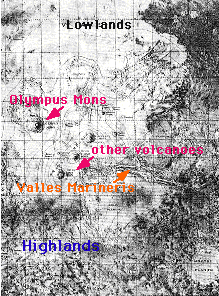
This map shows a portion of the surface of Mars.
Click on image for full size
Image from: NASA
Martian Global Geography
The surface of Mars can be broken into two main regions: highlands and lowlands. The highlands are in the southern hemisphere (the bottom of the figure), and the lowlands are in the northern hemisphere of Mars (top of the figure). The lowlands contain the
Tharsis Ridge, where many of the largest
volcanoes of Mars are located. Next to the Tharsis Ridge is
Valles Marineris, a very long canyon of Mars. The high resolution topographic map, which can be viewed by clicking on the image to the left, shows these regions in better detail. Measurements returned by Mars Global surveyor demonstrate the
severe height difference between these two regions of Mars.
The highlands are heavily cratered. They are the oldest portion of Mars. Even though the lowlands are younger, they do have craters and so have not really been resurfaced since the end of the period of cratering which marked the earliest portion of the history of the planet.
Not seen clearly in this image are the Martian polar caps. Besides ice, the southern polar region of Mars contains other interesting geologic features such as layered terrain and giant sanddunes. This region was suppose to be explored by the Mars '98 mission.
Careful examination of this map reveals no evidence of the kind of plate tectonics which can be seen in the Earth's crust.
You might also be interested in:
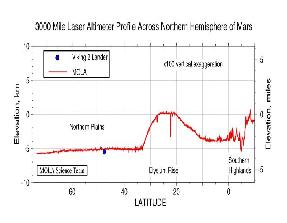
Mars Global Surveyor carries an instrument which measures the altitudes of things. The instrument is called an altimeter, or "altitude-meter". The graph to the left shows Mars Global Surveyor's measurement
...more
The Martian South Pole was first imaged by Mariner 7. The south polar region is part of the highlands of Mars, consisting of old, cratered terrain, and other interesting geologic features. The Mariner
...more
Geologists from the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C. have found empty lakes and a river in the highlands of Mars. They don't contain any water, but they may indicate that
...more
During its earliest history, Mars was bombarded with *planetismals*. The impacts of these asteroid-like boulders caused the surface regions of Mars to become warm enough for continents to drift across
...more
The European Space Agency (ESA) launched a mission to Mars called "Mars Express" in June of 2003. The Mars Express spacecraft has two parts: an orbiter that will circle Mars for at least one Martian year
...more
Isidis Planitia is flat plain within an ancient impact crater on the surface of Mars. Isidis Planitia is about 1500 km (930 miles) across. It is just north of the Martian equator near the center of the
...more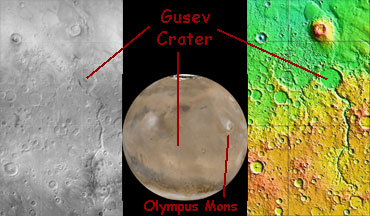
Gusev Crater is an impact crater on Mars that looks as though a lake may have once filled it in the distant past. One of the two Mars Exploration Rovers (MER) will explore Gusev Crater beginning in January
...more