This is an image of Tethys.
Click on image for full size
NASA/JPL
Tethys
Tethys was discovered by G. Cassini in 1684. Tethys is the 8th closest moon to Saturn.
Tethys is one of the icy moons. It is about as wide as the length of the Oregon coast.
Tethys is has a surface, with many craters, and also deep trenches.
You might also be interested in:

Icy moons are moons which are made of ice. These moons are unlike the earth's moon, which is made of rock. Perfect examples of icy moons are 3 of the Galilean satellites, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
...more
The surface of Tethys has many craters, which means that the surface is very old and hasn't been changed. But there is one region of Tethys which doesn't have many craters at all. The fact that there are
...more
This is an image of the Earth's moon, shown in the lower left, with the icy moons of Saturn. The moons in order, starting from the top left are: Mimas, Enceladus, Tethys, Dione, Rhea, and Iapetus.
...more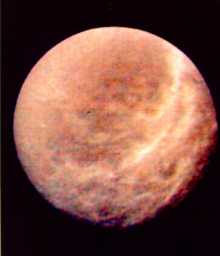
Rhea was discovered by G. Cassini in 1672. Rhea is the 5th farthest moon from Saturn. Rhea is one of the icy moons. Rhea is about as wide as the state of California is long. Rhea is has many craters and
...more
The planet Saturn has a lot of moons. It has a total of // Call the moon count function defined in the document head print_moon_count('saturn'); moons! Saturn also has huge rings which you can see in any
...more
Dione was discovered by G. Cassini in 1684. Dione is the 7th farthest moon from Saturn. It is a small icy moon, lightly cratered, with white streaks across the surface. Dione is about as wide as the Oregon
...more
The surface of Dione does not have many craters, which means that the surface has changed in the past. Instead of many craters, it has wispy white streaks like the ones on Rhea, which go for many kilometers
...more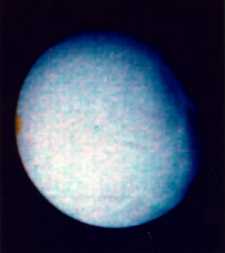
The surface of Enceladus does not have many craters. Instead it has grooves similar to those found on Ganymede. These grooves extend for many kilometers over the surface. The presence of grooves indicates
...more












