This is how an artist thinks the Phoebe ring might look if we could see it. The Spitzer space telescope spotted the Phoebe ring. Spitzer can "see" infrared "light". Saturn and the other rings are just a tiny dot compared to the Phoebe ring. The inset picture shows Saturn magnified.
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute.
The Phoebe Ring Around Saturn
The Phoebe Ring is one of the rings around the planet Saturn. The Phoebe Ring is much bigger than Saturn's other rings. It is about 100 times larger than the main ring system.
Saturn's moon Phoebe orbits within this ring. The ring is made up of tiny pieces of ice and dust. The ring particles probably come from Phoebe. They were probably knocked loose from Phoebe's surface by meteorite impacts over many, many years. Even though the Phoebe Ring is very large, there isn't much stuff in it. We can't see the Phoebe Ring in visible light, even using the world's most powerful telescopes. The Spitzer Space Telescope was able to detect the faint Phoebe Ring using infrared "light".
Saturn's main ring system is lined up with the planet's equator. The Phoebe Ring, on the other hand, is tilted 27°. Part of the Phoebe Ring crosses the orbit of another moon of Saturn, Iapetus. The surface of Iapetus is odd. Parts of the moon's surface are very bright, while other areas are very dark. Scientists think icy Iapetus is being splattered with dark particles from the Phoebe Ring. Phoebe itself has one of the darkest surfaces in our Solar System.
The ring was discovered by Anne Verbiscer and Michael Skrutskie of the University of Virginia and Douglas Hamilton of the University of Maryland. They announced their discovery on October 6, 2009.
You might also be interested in:

Many people like Saturn's rings. Although Saturn isn't the only planet with rings, it is the only planet famous for them. Almost every image or drawing of the planet has the rings included. But few people
...more
Meteors are streaks of light, usually lasting just a few seconds, which people occasionally see in the night sky. They are sometimes called "shooting stars" or "falling stars", though they are not stars
...more
Like the inner planets and Jupiter, Saturn is clearly visible in the night sky. The ancient Greeks named the planet after the god of agriculture and time. It wasn't until 1655, however, that we knew Saturn
...more
The dramatic appearance of Saturn stems mainly from the spectacular rings. The atmosphere looks much less dramatic. The clouds of Saturn are much less colorful than those of Jupiter. This is because the
...more
The Giant planets do not have the same layered structure that the terrestrial planets do. Their evolution was quite different than that of the terrestrial planets, and they have less solid material. Saturn's
...more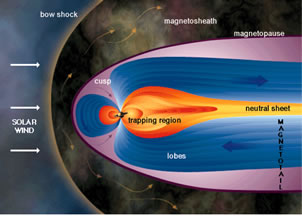
Saturn's magnetosphere is not as big as Jupiter's, but it is still pretty big. It is big enough to hold all of Saturn's moons. It is probably made the same way as is Jupiter's, which affects its overall
...more
There's a lot of strange and interesting stuff going on at both the North and South Poles of Saturn. Two of Saturn's moons also have interesting polar regions. Let's take a look! The atmosphere and clouds
...more















