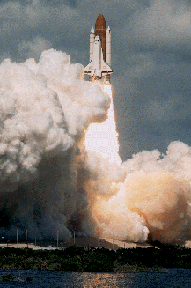
Photograph of Atlantis lift-off.
Click on image for full size
NASA/JPL
Leaving Earth
The average person can jump about 2 feet off the ground, and few of us can throw a baseball higher than even fifty feet in the air. It seems as if there is some force that "pulls" everything on the Earth down to the ground.
This "pull" is due to gravity, an attractive force which exists between any two objects, but is dependent on their size. Since our planet is so massive, we experience a strong pull toward its center.
Space travel is only possible is if we can escape Earth's gravitational field. However, for a spacecraft to do so it must reach a velocity of 11 km/sec (7 miles/sec), or 39,600 km/hr (nearly 25,000 mph). It was only by the middle of the twentieth century that mankind finally understood enough about rocketry to make such high speeds attainable.
Today, spacecraft can also be carried into space by a shuttle, which releases them while in orbit. After leaving Earth's gravitational field, spacecraft then use small on-board thrusters to navigate through space and explore the universe.
You might also be interested in:

A new museum exhibit shows that some of the robots, vehicles and devices from the Star Wars films are close to the types of things scientists have developed to use in space. The exhibition--at the Science
...more
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was one of the most important exploration tools of the past two decades, and will continue to serve as a great resource well into the new millennium. The HST found numerous
...more
Driven by a recent surge in space research, the Apollo program hoped to add to the accomplishments of the Lunar Orbiter and Surveyor missions of the late 1960's. Apollo 11 was the name of the first mission
...more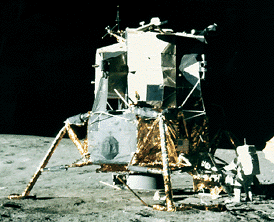
Apollo 12 was launched on Nov. 14, 1969, surviving a lightning strike which temporarily shut down many systems, and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended
...more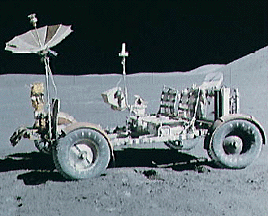
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon
...more
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program on July 7, 1999. The Discovery program specializes in low-cost, scientific projects. In May 2001, Deep Impact was given
...more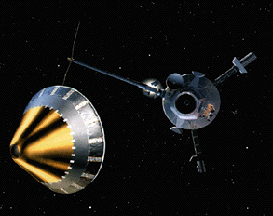
The Galileo spacecraft was launched on October 19, 1989. Galileo had two parts: an orbiter and a descent probe that parachuted into Jupiter's atmosphere. Galileo's main mission was to explore Jupiter and
...more