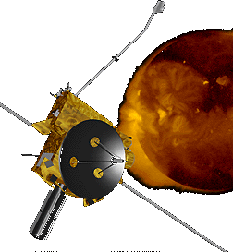
The Ulysses spacecraft studies the Sun.
NASA
How Scientists Study Space Weather
Scientists combine various techniques to study space weather. Earth-based
and orbiting telescopes constantly observe the Sun in many different wavelengths.
Both satellites and ground-based instruments contribute readings of space
weather features such as particle densities, magnetic field strengths, and
radiation intensities. Scientists develop complex mathematical
models based on the laws of physics to predict behaviors of space
weather systems. Space physicists have also developed metrics, such as sunspot counts, to quantitatively describe variations in space weather.
Because of the complexity of space weather systems, scientists often use models to try to understand and predict the systems. Some models describe the Sun,
others interplanetary space, and still others cover the Earth's magnetosphere or its upper atmosphere. Sophisticated computer software crunches the numbers
generated by these models so scientists can compare their predictions with
observed events.
We have only been making direct observations of the Sun and space weather phenomena using telescopes, satellites, and other sophisticated instruments for a relatively short period of time. The Sun, however, has been around for several billion years. Scientist use various "proxy" techniques to estimate levels of solar and space weather activity in prehistoric times and in more recent eras prior to the space age.
You might also be interested in:
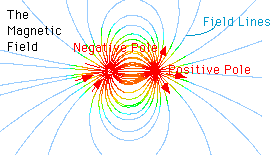
The force of magnetism causes material to point along the direction the magnetic force points. This property implies that the force of magnetism has a direction. As shown in the diagram to the left, the
...more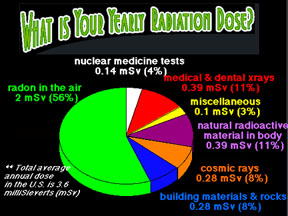
Radiation comes in two basic types: electromagnetic radiation transmitted by photons, and particle radiation consisting of electrons, protons, alpha particles, and so forth. Electromagnetic radiation,
...more
Sunspots are dark, planet-sized regions that appear on the "surface" of the Sun. Sunspots are "dark" because they are cooler than their surroundings. A large sunspot might have a central temperature of
...more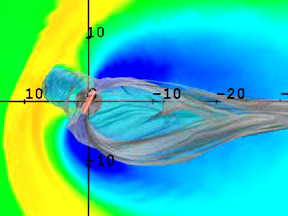
Scientists who study space weather make extensive use of computer models to make sense of complex phenomena. This is a way in which space weather is quite similar to Earthly weather, for weather forecasters
...more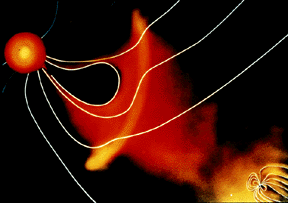
The Sun is surrounded by a "bubble" in space called the heliosphere. In a sense, we Earthlings live within the outer atmosphere of our Sun. The solar wind fills the heliosphere with energetic
...more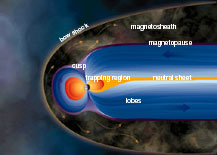
The Earth has a magnetic field with north and south poles. The magnetic field of the Earth is enclosed in a region surrounding the Earth called the magnetosphere. As the Earth rotates, its hot core generates
...more
The thermosphere is a layer of Earth's atmosphere. The thermosphere is directly above the mesosphere and below the exosphere. It extends from about 90 km (56 miles) to between 500 and 1,000 km (311 to
...more