The M1 supernova photographed by the Hubble telescope
University of Oregon, The Electronic Universe Project
The Supernova
A Supernova is
a very massive star that explodes at the end of its life
cycle. The supernova is the furnace where the heavy elements
(heavier than iron) are formed.
You might also be interested in:
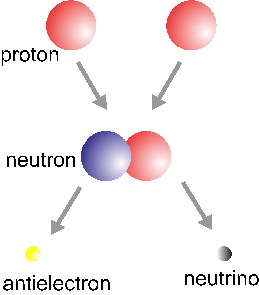
In the basic Hydrogen fusion cycle, four Hydrogen nuclei (protons) come together to make a Helium nucleus. This is the simple version of the story. There are actually electrons, neutrinos and photons involved
...more
Fusion in the core of stars is reached when the density and temperature are high enough. There are different fusion cycles that occur in different phases of the life of a star. These different cycles make
...more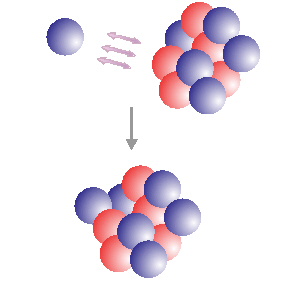
Neutron capture can occur when a neutron approaches a nucleus close enough for nuclear forces to be effective. The neutron is captured and forms a heavier isotope of the capturing element. When the new
...more
A Supernova is a very massive star that explodes at the end of its life cycle. The supernova is the furnace where the heavy elements (heavier than iron) are formed.
...more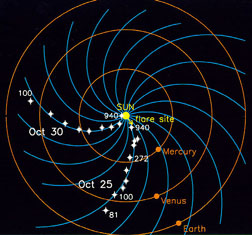
IMF stands for Interplanetary Magnetic Field. It is another name for the Sun's magnetic field. The Sun's magnetic field is huge! It goes beyond any of the planets. The Sun's magnetic field got its name
...more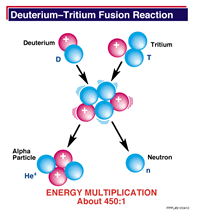
Nuclear fusion is a process where two or more nuclei combine to form an element with a higher atomic number (more protons in the nucleus). Fusion is the reverse process of nuclear fission. Fusion reactions
...more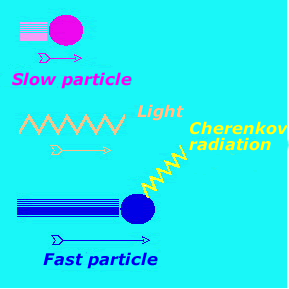
The theory of relativity states that no particle can travel at the speed of light in a vacuum. However, light travels at lower speeds in dense media, like water. A particle traveling in water must have
...more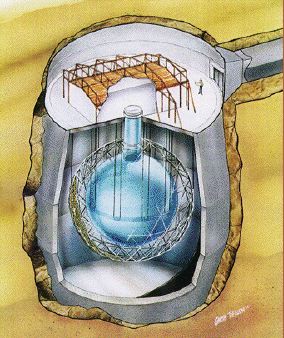
Neutrino interactions with matter are extremely rare, so detecting a neutrino is very hard. Neutrino detectors are typically large, underground tanks filled with a fluid that reacts to the passage of neutrinos.
...more














