The Sun's radiative zone lies between the incredibly hot core and the outer convective zone.
Click on image for full size
The Sun's Radiative Zone
The Sun's radiative zone is the section of the solar
interior between the innermost core and
the outer convective
zone. In the radiative zone, energy generated by nuclear
fusion in the core moves outward as electromagnetic
radiation. In other words, the energy is conveyed by photons.
When the energy reaches the top of the radiative zone, it begins to move
in a different fashion in the convective zone. In the convective zone, heat
and energy are carried outward along with matter in swirling flows called
convection cells. This motion is similar to the roiling flows seen in a pot
of boiling water.
The inner parts of the Sun (core and radiative
zone) spin
differently than the outer layers (convective zone). The boundary between
these two types of rotation, which lies between the radiative and convective
zones, is called the tachocline.
Many other stars also have radiative zones. The Sun's radiative zone extends
from the core outward to about 70% of the Sun's radius. In a smaller (than
the Sun) star that is cooler than our Sun, the convective zone tends to be
larger, extending deeper into the star's interior. Thus the radiative zone
tends to be smaller. In very small, cool stars the convective zone may reach
all the way to the star's core, and there may be no radiative zone at all.
In a larger (than the Sun) star with a higher temperature, the radiative zone
tends to be larger and the convective zone smaller. Especially large, hot stars
may not have a convective zone at all - their radiative zone may extend all
the way from the core to the star's surface.
You might also be interested in:
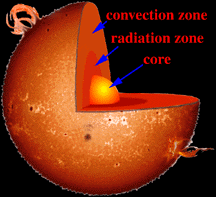
To understand how our Sun works, it helps to imagine that the interior of the Sun is made up of different layers, one inside the other. The innermost layer, the solar core, is the region where the energy
...more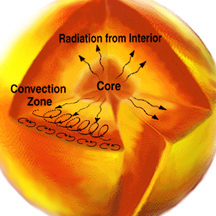
The convection zone in the Sun occurs above the radiative zone, at about .7 to .8 solar radii from the center of the Sun. At this point the temperature gradient (the change in temperature with depth)
...more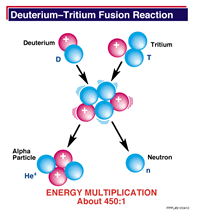
Nuclear fusion is a process where two or more nuclei combine to form an element with a higher atomic number (more protons in the nucleus). Fusion is the reverse process of nuclear fission. Fusion of light
...more
What are the "parts" of the Sun? The photosphere, the visible "surface" of the Sun, defines the outermost boundary of the "inside" of the Sun. The three main regions of the
...more
The Sun's radiative zone is the section of the solar interior between the innermost core and the outer convective zone. In the radiative zone, energy generated by nuclear fusion in the core moves outward
...more
IMF stands for Interplanetary Magnetic Field. It is another name for the Sun's magnetic field. The Sun's magnetic field is enormous and is carried by the solar wind. The solar wind and magnetic field are
...more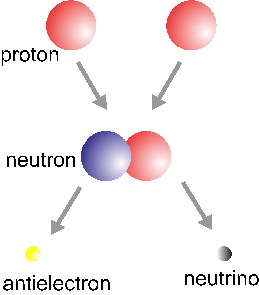
The basic Hydrogen fusion cycle involves four Hydrogen nuclei (protons) and two electrons and yields a Helium nucleus, two neutrinos and six photons. This process occurs in three steps: the first one is
...more
Fusion in the core of the stars is achieved when the density and temperature arising from the gravitational pressure are high enough. There are different fusion cycles that occur in different phases of
...more












