The Fate of the Sun
In about 5 billion years, the hydrogen in the center of the Sun
will start to run out. The helium will get squeezed. This will
speed up the hydrogen burning. Our star will slowly puff into a
red
giant. It will eat all of the inner planets, even the Earth.
As the helium gets squeezed, it will soon get hot enough to burn into
carbon. At the same time, the carbon can also join helium to form oxygen.
The Sun is not very big compared to some stars. It will never get hot
enough in the center to burn carbon and oxygen. These elements will
collect in the center of the star. Later it will shed most of its outer
layers, creating a planetary nebula, and reveal a hot
white dwarf star.
Nearly 99 percent of all stars in the galaxy will end their lives as white
dwarfs. By studying the stars that have already changed, we can learn
about the fate of our own Sun.
You might also be interested in:
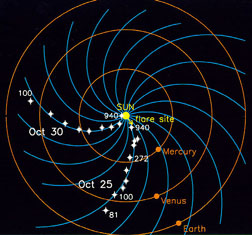
IMF stands for Interplanetary Magnetic Field. It is another name for the Sun's magnetic field. The Sun's magnetic field is huge! It goes beyond any of the planets. The Sun's magnetic field got its name
...more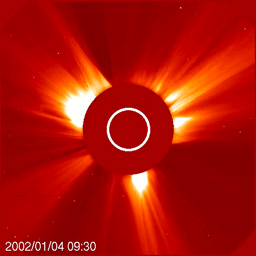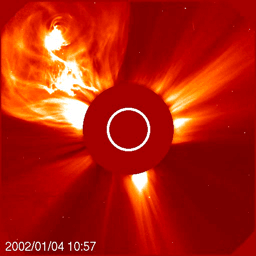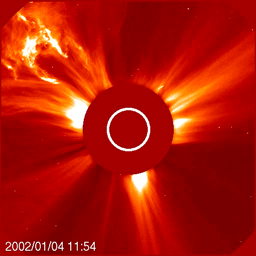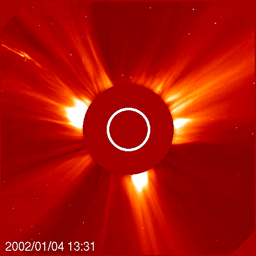
"Without warning, the relatively calm solar atmosphere can be torn asunder by sudden outbursts of a scale unknown on Earth. Catastrophic events of incredible energy...stretch up to halfway across the visible
...more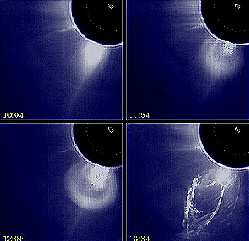
The Sun is not a quiet place, but one that exhibits sudden releases of energy. One of the most frequently observed events are solar flares: sudden, localized, transient increases in brightness that occur
...more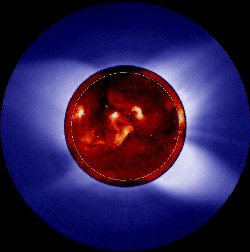
The visible solar atmosphere consists of three regions: the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the solar corona. Most of the visible (white) light comes from the photosphere, this is the part of the Sun
...more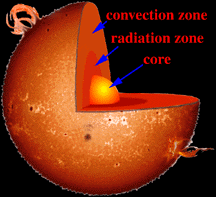
To understand how our Sun works, it helps to imagine that the inside of the Sun is made up of different layers, one inside the other. The core, or the center of the Sun, is the region where the energy
...more
Scientists at the High Altitude Observatory (HAO) try to understand the changes we see in the Sun over time. They also study how these changes affect the atmosphere of the Earth. There are four main areas
...more
Energy from the Sun affects many things on Earth. One of the main things the Sun does is warm our planet, including the atmosphere. This energy drives much of our weather. The solar cycle, the rise and
...more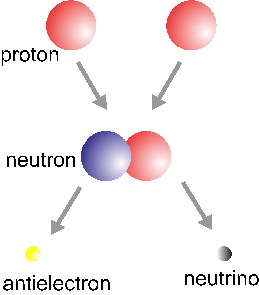
In the basic Hydrogen fusion cycle, four Hydrogen nuclei (protons) come together to make a Helium nucleus. This is the simple version of the story. There are actually electrons, neutrinos and photons involved
...more















