Coastal carvings: The Big Sur coastline in California is the result of a great geological uplifting, which occurred roughly 30 million years ago.
Image courtesy of Kip F. Evans
Ocean Literacy - Essential Principle 2
The ocean and life in the ocean shape the features of the Earth.
Fundamental Concept 2a.
Many earth materials and geochemical cycles originate in the ocean. Many of the sedimentary rocks now exposed on land were formed in the ocean. Ocean life laid down the vast volume of siliceous and carbonate rocks.
Fundamental Concept 2b.
Sea level changes over time have expanded and contracted continental shelves, created and destroyed inland seas, and shaped the surface of land.
Fundamental Concept 2c.
Erosion—the wearing away of rock, soil and other biotic and abiotic earth materials—occurs in coastal areas as wind, waves, and currents in rivers and the ocean move sediments.
Fundamental Concept 2d.
Sand consists of tiny bits of animals, plants, rocks and minerals. Most beach sand is eroded from land sources and carried to the coast by rivers, but sand is also eroded from coastal sources by surf. Sand is redistributed by waves and coastal currents seasonally.
Fundamental Concept 2e.
Tectonic activity, sea level changes, and force of waves influence the physical structure and landforms of the coast.
You might also be interested in:

The sediment in an organic sedimentary rock is made of fossils! The mineral parts of animals, such as bones and shells, are much more likely to be preserved than the soft tissues, which typically decay.
...more
Like other types of sedimentary rocks, chemical rocks form at the Earth’s surface, are usually found in horizontal layers, and do not form from molten rock. However, unlike most other sedimentary rocks,
...more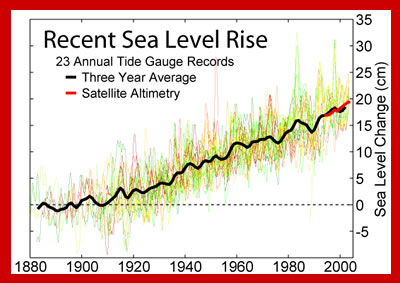
The low-lying coast of Bangladesh in South Asia is home to millions of people, yet the amount of sea level rise predicted for the 21st Century is expected to change that, flooding homes with seawater and
...more
Sneeze into a pile of dust and the particles fly everywhere. Sneeze into a pile of rocks and they stay put. That’s because they have more mass. You need more force than a sneeze to move those rocks. Wind
...more
Wind is moving air. Warm air rises, and cool air comes in to take its place. This movement creates different pressures in the atmosphere which creates the winds around the globe. Since the Earth spins,
...more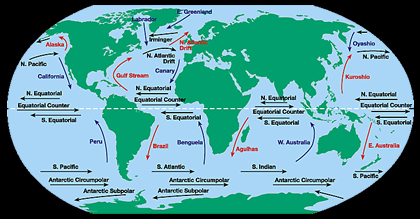
The water at the ocean surface is moved primarily by winds. Large scale winds move in specific directions because they are affected by Earth’s spin and the Coriolis Effect. Because Earth spins constantly,
...more
Rivers are very important to Earth because they are major forces that shape the landscape. Also, they provide transportation and water for drinking, washing and farming. Rivers can flow on land or underground
...more















