Click on image for full size
Courtesy of Lisa Gardiner
Related links:
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
Rising Temperature in Large Lakes
Greenland's Ice Is Melting Faster
Tropics May Be Next Hotspot for Disease Outbreaks (Podcast from NSF)
Global Warming Affects World's Largest Freshwater Lake
Movie: Is Climate Change Involved with Amphibian Deaths?
A New Plan to Help Earth’s Changing Climate
Exploring Ocean Dead Zones video
Fossil Record Suggests Insect Assaults Foliage May Increase with Warming Globe
Our Changing Planet - Key Indicators of Climate Change
Wildfires - Why are they a challenge to stop? Classroom Activity
Effects of Climate Change Today
The world's surface air temperature increased an average of 0.6° Celsius (1.1°F) during the last century according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). This may not sound like very much of a temperature change, but it is. And the warmer temperature is causing noticeable changes to our planet. Below are some effects of climate change that we see happening.
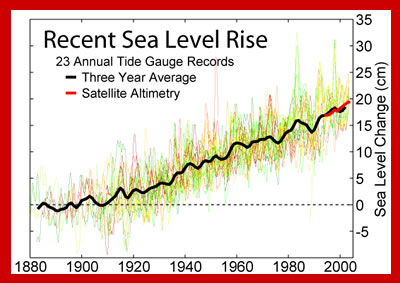
- Sea level is rising. During the 20th century, sea level rose about 15 cm (6 inches) due to melting glacier ice and expansion of warmer seawater. Models predict that sea level may rise as much as 59 cm (23 inches) during the 21st Century, threatening coastal communities, wetlands, and coral reefs.
- Arctic sea ice is melting. The summer thickness of sea ice is about half of what it was in 1950. Melting ice may lead to changes in ocean circulation. Melting ice speeds up warming of the Arctic because water absorbs more heat than ice.
- Glaciers and permafrost are melting. Over the past 100 years, mountain glaciers in all areas of the world have decreased in size and so has the amount of permafrost in the Arctic. Greenland's ice sheet is melting faster too.
- Sea-surface temperatures are warming. Warmer waters in the shallow oceans have contributed to the death of about a quarter of the world's coral reefs in the last few decades. Many of the coral animals died after weakened by coral bleaching, a process tied directly to warmed waters.
- The temperatures of large lakes are warming. The temperatures of large lakes world-wide have risen dramatically. Temperature rises have increased algal blooms in lakes, favor invasive species, increase stratification in lakes and lower lake levels.
- Heavier rainfall cause flooding in many regions. Warmer temperatures have led to more intense rainfall events in some areas. This can cause flooding.
- Extreme drought is increasing. Higher temperatures cause a higher rate of evaporation and more drought in some areas of the world. Areas that are currently prone to drought are expected to become even drier over the next century.
- Crops are withering. Increased temperatures and extreme drought are causing a decline in crop productivity around the world. Decreased crop productivity can mean food shortages which have many social implications.
- Ecosystems are changing. As temperatures warm, species may either migrate to a cooler, more suitable habitat or die. Species that are particularly vulnerable include endangered species, coral reefs, and polar animals. Warming has also caused changes in the timing of spring events and the length of the growing season.
- Hurricanes have changed in frequency and strength. There is evidence that the number of intense hurricanes has increased in the Atlantic since 1970. This may also be true for tropical cyclones in other parts of the world. Scientists continue to study whether climate is the cause.
- More frequent heat waves. It is likely that heat waves have become more common in more areas of the world.
- Warmer temperatures affect human health. There has been an increase in heat-related deaths, some changes in the ranges of animals that carry disease like mosquitoes, and an increase in the length of the pollen season.
- Seawater is becoming more acidic. Carbon dioxide dissolving into the oceans, is making seawater more acidic. There could be impacts on coral reefs and other marine life.
According to computer models, more global warming is in our future. If we continue to emit as many, or more, greenhouse gases, this will cause much more warming during the 21st century than we saw in the 20th century. During the 21st century, various computer models predict that Earth's average temperature will rise between 1.8 and 4.0° Celsius (3.2° and 7.2° F).