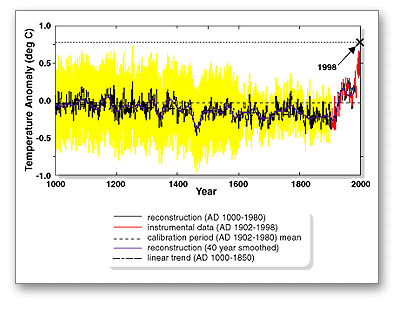
Change in Earth's average global temperature over the past 1000 years showing that during the Medieval Warm Period (950-1100A.D.) temperatures were likely similar to the first part of the 20th century, climate cooled during the Little Ice Age (1350-1850), and has warmed dramatically in recent decades.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of NOAA
The Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period was a time of warm climate in Europe. The warmest part of the Medieval Warm Period was from about 950 until 1100 A.D. The warm climate overlaps with a time of high solar activity called the Medieval Maximum. The Medieval Warm Period occurred before the Little Ice Age, a time of cool climate in Europe and other places around the world. The graph on the left shows a reconstruction of average global temperatures over the past 1000 years with temperatures during the Medieval Warm Period similar to the first part of the 20th Century, cooler temperatures during the Little Ice Age, and dramatic warming in recent decades. The Medieval Warm Period was likely cooler than the past few decades.
According to some archaeologists, the Vikings may have been better able to explore and colonize many areas in Northern Europe while the climate was relatively warm during the Medieval Warm Period because there was less sea ice. They traveled by boats to Greenland among other places through seas that would later become blocked by sea ice during the Little Ice Age.
Last modified November 14, 2007 by Lisa Gardiner.
You might also be interested in:

The Little Ice Age was a time of cooler climate in most parts of the world. Although there is some disagreement about exactly when the Little Ice Age started, records suggest that temperatures began cooling
...more
Sea ice is frozen seawater. It can be several meters thick and it moves over time. Although the salts in the seawater do not freeze, pockets of concentrated salty water become trapped in the sea ice when
...more
Leaders from 192 countries are meeting in Copenhagen, Denmark December 7-18, 2009 to decide how the world will deal with climate change. They are trying to decide how to limit the amount of greenhouse
...more
The climate where you live is called regional climate. It is the average weather in a place over more than thirty years. To describe the regional climate of a place, people often tell what the temperatures
...more
Even though only a tiny amount of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse gases, they have a huge effect on climate. There are several different types of greenhouse gases. The major ones are carbon
...more
Satellites that orbit Earth help us study Earth's atmosphere, weather, and climate. Here are a few of the many spacecraft that study our atmosphere. Aura was launched in July 2004. It is studying pollution,
...more
To figure out the future of climate change, scientists need tools to measure how Earth responds to change. Some of these tools are global climate models. Using models, scientists can better understand
...more