Glossary : Ultraviolet Radiation
The energy range just beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
Although ultraviolet radiation constitutes only about 5 percent of the
total energy emitted from the sun, it is the major energy source for the
stratosphere and mesosphere, playing a dominant role in both energy
balance and chemical composition.
Most ultraviolet radiation is blocked by Earth's atmosphere, but some
solar ultraviolet penetrates and aids in plant photosynthesis and helps
produce vitamin D in humans. Too much ultraviolet radiation can burn the
skin, cause skin cancer and cataracts, and damage vegetation.
You might also be interested in:

As we move out in the solar system, the planets get colder, and higher temperatures begin to be found deeper into the interior of the planet, where the pressure of overlying material becomes immense. Jupiter's
...more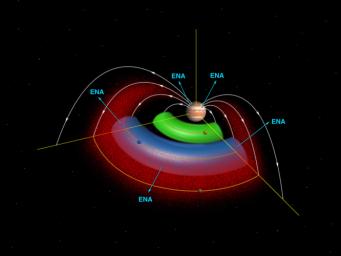
The Galileo mission discovered an amazing thing. Europa has its own atmosphere, although it is very, very thin. This atmosphere is created when fast moving molecules in Jupiter's magnetosphere hit the
...more
AU stands for Astronomical Units. Distances in space are too large to measure in Earth standards like miles or kilometers. For distances too large to measue in AU, we use light years. A light year is the
...more
The solar wind is formed as the Sun's topmost layer blows off into space carrying with it magnetic fields still attached to the Sun. Gusts and disturbances form in the solar wind associated with violent
...more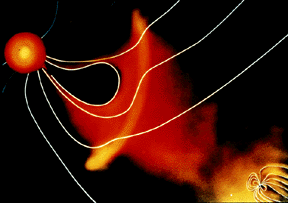
For a planet to be affected by a blob of material being ejected by the sun, the planet must be in the path of the blob, as shown in this picture. The Earth and its magnetosphere are shown in the bottom
...more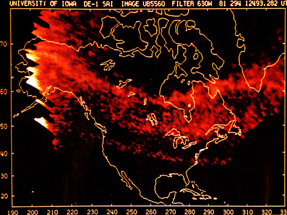
The aurora we are most familiar with is the polar aurora. This is what people are referring to when they speak of the northern or southern lights. But there are other less-known auroral activity, such
...more
This figure shows the effect of the aurora on the atmosphere. When FAC's enter the atmosphere and create the aurora, they warm the atmosphere impulsively. This impulse travels throughout the atmosphere
...more














