Scientists measure carbon dioxide from soils in the greenhouse warming experiment.
Click on image for full size
Image Courtesy of Steven D. Allison
Soil Microbes Produce Less Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Than Expected With Global Warming
Scientists have learned that microbes that live in the soil, like fungi and bacteria, don't produce more carbon dioxide when the climate is warmer. In fact, at first these microbes will produce more carbon dioxide, but then they overheat and grow more slowly. Eventually this means they produce fewer greenhouse gases that are responsible for a warming climate.
According to a scientist named Steve Allison, "In a balanced environment, plants store carbon in the soil and microbes use that carbon to grow. Enzymes produced by microbes convert soil carbon into atmospheric carbon dioxide."
Allison developed a computer model to test what might happen to the carbon cycle when microbes change in response to climate change. The model he created showed that microbes became less productive as the climate warmed. A warming climate made their growth slow and they produced fewer enzymes.
"We need to develop more models to include microbe diversity," Allison said. "But the general principle that's important in our model is the decline of carbon dioxide production after an initial increase."
You might also be interested in:
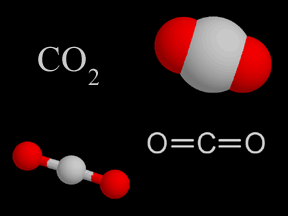
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a kind of gas. There isn't that much carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, but it is still very important. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. That means it helps trap heat coming
...more
Even though only a tiny amount of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse gases, they have a huge effect on climate. There are several different types of greenhouse gases. The major ones are carbon
...more
To figure out the future of climate change, scientists need tools to measure how Earth responds to change. Some of these tools are global climate models. Using models, scientists can better understand
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. "The data will help give us a better road map to what a future
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core, and makes up about 84 percent of the Earth's volume. The mantle is made up of many distinct portions or
...more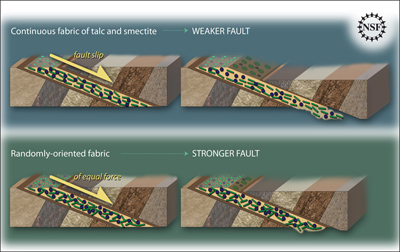
Some geologic faults that appear strong and stable, slip and slide like weak faults, causing earthquakes. Scientists have been looking at one of these faults in a new way to figure out why. In theory,
...more
The sun goes through cycles that last approximately 11 years. These solar cycle include phases with more magnetic activity, sunspots, and solar flares. They also include phases with less activity. The
...more















