The Size of the Planet Matters
|
Mercury
(small) |
Venus
(medium sized) |
Jupiter
(very large) |
|
|
|
|
| Hydrogen (H) |
less than 1 hour |
days |
over the age of the Universe |
|
|
|
|
| Helium (He) |
roughly 1 day |
100 times the age of the solar system |
over the age of the Universe |
|
|
|
|
| Oxygen (O) |
800 million years |
over the age of the Universe |
over the age of the Universe |
|
|
|
|
Scientists think that the original air of many earth-like planets drifted away, and the air they have today came out from inside the planet.
This table shows the time it takes for some of the molecules of the air to escape from a planet. The table shows that as the planets get bigger, it is harder for the molecules to escape.
The table shows that the average time for any molecules to escape from Jupiter's gravity is much too long. Therefore probably all the molecules in Jupiter's atmosphere are the same ones drawn to the planet when it was forming.
 Return to atmosphere
Return to atmosphere
You might also be interested in:

The giant planets have definitely changed since their formation. But how much remains to be seen. Most of the original air of the giant planets remains in place. (The earth-like planets lost most of their
...more
The mesosphere of Jupiter is a region of balance between warming and cooling. That essentially means that nothing happens there. Except for diffusion, the atmosphere is still. Upper reaches of the atmosphere,
...more
As on Earth, the atmosphere of Jupiter consists of a troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. The troposphere is the region where the visible clouds are to be found. The stratosphere, as
...more
The stratosphere of Jupiter is a region of warming as determined by infrared measurements of methane (CH4) in the region. Like the troposphere, the stratosphere is warmed by the sun, warmed by Jupiter's
...more
The troposphere of Jupiter is where the clouds are. Clouds form in regions of strong atmospheric motion, when condensation takes place. The troposphere is the region rapidly stirred by vertical motions.
...more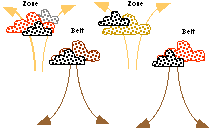
On Jupiter, the winds in the belts and zones blow first in one direction, then in the opposite direction. Wind blows east in a belt, and west in a zone. The clouds rise up in a belt, and drop down in a
...more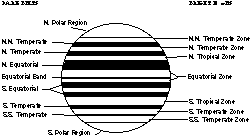
The striped cloud bands on Jupiter are certainly not as straight as they appear to be in this picture! The picture shows that the striped pattern is divided into belts and zones. The belts and zones of
...more















