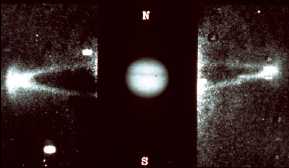
This image shows a radio map of Jupiter taken in the inner regions of the plasmasphere.
Click on image for full size
JPL
Jupiter's Plasmasphere
Jupiter's magnetosphere is practically all plasmasphere. Jupiter's magnetosphere is filled with plasma. Most of the plasma comes from the donut-shaped cloud (torus) of material from Io.
Particles enter the plasmasphere from the atmosphere as well as the magnetotail. Particles leave the plasmasphere at the north and south poles. When these particles collide with the atmosphere, they create the aurora.
Jupiter's plasmasphere makes powerful radio noises. Radio signals and other waves which come from the plasmasphere include whistler waves, chorus and hiss.
You might also be interested in:
A satellite which has an atmosphere, such as Jupiter's moon Io, and which also is inside a magnetosphere (unlike the Earth's moon), will leave a cloud of particles behind as it orbits the planet. This
...more
Radio noises are a signature of activity within the magnetosphere. There are many kinds of radio waves in Jupiter's environment. These are: DAM DAM is the most intense of Jupiter's radio signals. It is
...more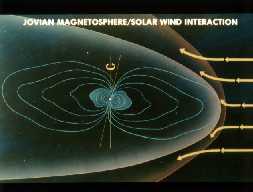
Jupiter's magnetosphere is very pointed and bullet-shaped, as shown in this picture, because of the nature of how it is created. The magnetosphere has many parts, such as the bow shock, magnetospheath,
...more
Jupiter's magnetosphere is practically all plasmasphere. Jupiter's magnetosphere is filled with plasma. Most of the plasma comes from the donut-shaped cloud (torus) of material from Io. Particles enter
...more
Anthony Wesley is an astronomer in Australia. One night in July 2009, Wesley noticed a dark spot on Jupiter that hadn't been there before. He had discovered the remains of a huge impact on Jupiter! A comet
...more
The giant planets have definitely changed since their formation. But how much remains to be seen. Most of the original air of the giant planets remains in place. (The earth-like planets lost most of their
...more
The mesosphere of Jupiter is a region of balance between warming and cooling. That essentially means that nothing happens there. Except for diffusion, the atmosphere is still. Upper reaches of the atmosphere,
...more













